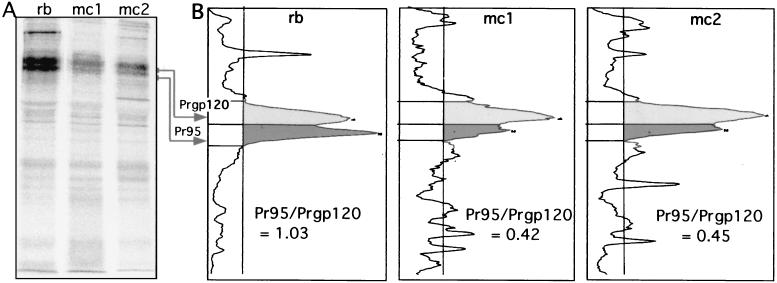
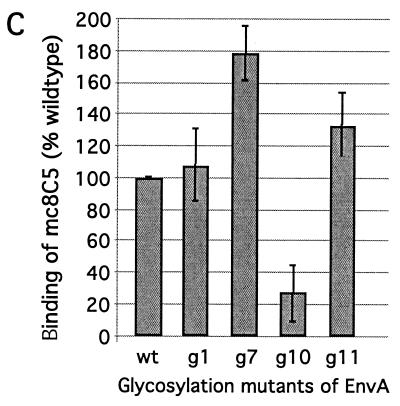
FIG. 7.
Recognition and binding of EnvA by mc8C5-4 is modulated by glycosylation. (A and B) IP. Df-1 cells expressing the cleavage mutant EnvA-S19 were metabolically labeled, lysed in nondenaturing buffer, and divided into three samples. One was immunoprecipitated with 1 μl of rb-anti-A-tail serum plus staphylococcus A (rb), and two were immunoprecipitated with 5 μl of mc8C5-4 ascites and either protein G (mc1) or 2 μl of rb-anti-mouse IgG plus staphylococcus A (mc2). (A) Samples were analyzed by autoradiography following SDS-PAGE; quantitation of the specific bands for Pr95 precursor and Prgp120 fully glycosylated precursor was performed with an OptiQuant scanner and software. (B) Profiles are shown, and the ratios of Pr95 to Prgp120 per sample are indicated. (C) FACS assay. Binding of mc8C5-4 to selected EnvA glycoproteins harboring glycosylation deletion mutations in the SU subunit (11) was analyzed after transient transfection of 293T cells with cDNA. Cells were treated for FACS analysis as described in Materials and Methods, using either Ngp37, a polyclonal antibody against the EnvA TM domain (31), or mc8C5-4, directed against SU-A as primary antibody. Mean fluorescence values as a measure of mc8C5-4 binding to EnvA wild-type and mutants were corrected for potential differences in EnvA surface expression by normalizing with the values obtained from the Ngp37-incubated duplicate samples.