Fig. 2. Characterization of GCAP1 and its mutants.
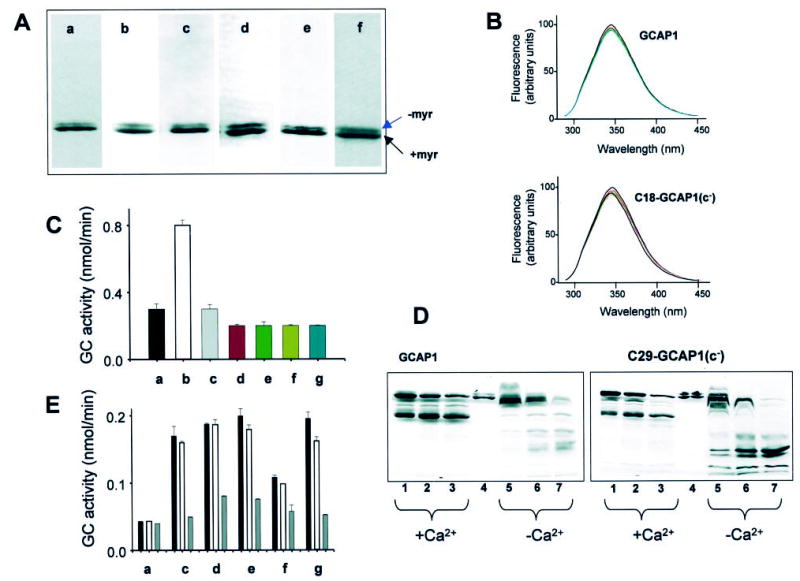
A, SDS-PAGE of GCAP1 (a) and most extensively used mutants in this study, C18-GCAP1(c−) (b), C29-GCAP1(c−) (c), C106-GCAP1(c−) (d), C125-GCAP1(c−) (e), and C29S-GCAP1 (f). Similar electrophoretic patterns were observed for other mutants. B, fluorescence emission spectra of GCAP1 and C18-GCAP1(c−). Fluorescence spectra (30) were measured as a function of [Ca2+], from 10−10 m (solid line) and at [Ca2+] = 10−6 m (red dashed line; [Ca2+] chosen as in Fig. 3). The emission spectra of GCAP1 and the mutant were recorded using λex =280 nm. There is no significant change in spectral shape for GCAP1 and C18-GCAP1(c−), both at 2 μm and atany [Ca2+]. Similarly, all other mutants showed only minor changes in their intrinsic fluorescence. The fluorescence titration was reproducible in two independent experiments for each mutant. C, competition assay of GCAP1 and mutants GCAP1(E75Q,E111Q,E155Q)(32) at high [Ca2+]. The GC activity was measured using washed ROS (a) in the presence of the constitutively active mutants (1 μg) at 2 μm [Ca2+] (b), and the presence of GCAP1 (c) (2 μg) and most extensively used mutants in this study, C18-GCAP1(c−) (d) (2 μg for this and other mutants), C29-GCAP1(c−) (e), C106-GCAP1(c−) (f), and C125-GCAP1(c−) (g). D, limited proteolysis of GCAP1 and C29-GCAP(c−) by trypsin. The digestion was carried out at 30 °C at a ratio of GCAP1s/trypsin 300:1, and the digest was analyzed by SDS-PAGE at 5 min (lanes 1 and 5), 10 min (lanes 2 and 6), and 16 min (lanes 3 and 7). +Ca2+represents 2 μm [Ca2+], and −Ca2+ indicates 30 nm [Ca2+]. Lane 4 represents undigested GCAP. All other mutants displayed similar digestion patterns, although the varied levels of the proteolytic fragments resulted from different amount of GCAP1 mutants in the assay. E, stability of GCAP1 and its mutants. The GC activity was measured using washed ROS as a source of GC (a) in the presence of 0.5 μg of GCAP1 (c) at 30 nm [Ca2+]. The black bar represents GCAP not exposed to heat treatment (open bar and gray bar), GCAP1 preincubated for 15 min at 50 °C or 100 °C, respectively. Other mutants C18-GCAP1(c−) (d), C29-GCAP1(c−) (e), C106-GCAP1(c−) (f), and C125-GCAP1(c−) (g) were treated in the similar conditions. The varied levels of the GC stimulating activity resulted from different amounts of GCAP1 mutants in the assays.
