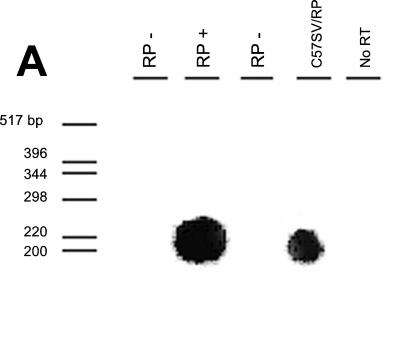
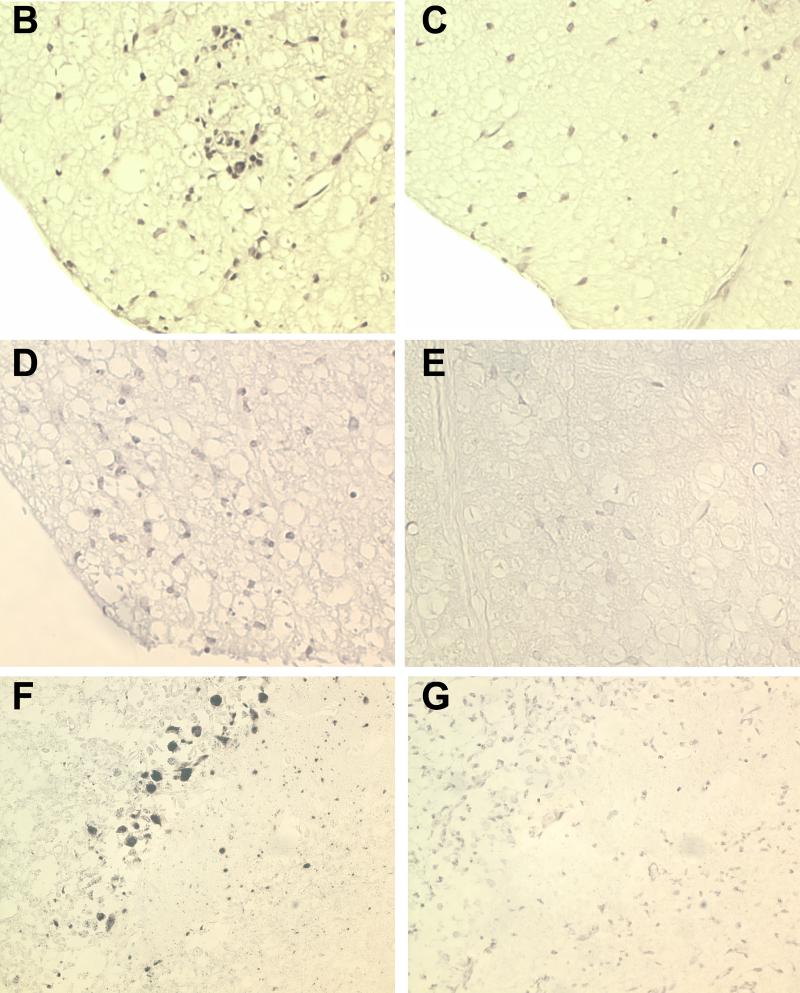
FIG. 2.
TMEV coding region mRNA expression in transgenic mice. (A) Expression of RP transgene after stimulation with gamma interferon, as detected by RT-PCR followed by Southern blotting, was low but detectable. Examples of expression for the RP transgene are shown for both a transgene-positive B10 mouse (second lane from left) and transfected C57SV cells (fourth lane from left). (B and C) In situ hybridization to detect Kb-LP mRNA was performed on spinal cords of LP+ transgenic mice (B) and spinal cords of LP− littermate control mice (C). (D and E) In situ hybridization to detect Kb-VP1 mRNA was performed on spinal cords of VP1+ transgenic mice (D) and spinal cords of VP1− littermate control mice (E). To demonstrate the stringency by which the Kb-VP1 probe hybridizes to mRNA expressed by the Kb-VP1 transgene alone, the in situ experiment was repeated on the brains of 7-day-infected nontransgenic C57BL/10 mice. (E and F) Using anti-TMEV immunostaining, the hippocampus of 7-day-infected C57BL/10 mice stained positive for detection of TMEV infection (F) but negative for in situ detection of Kb-VP1 mRNA (E). Note that, as shown in panel E, the Kb-VP1 probe used to detect Kb-VP1 mRNA did not hybridize with Kb or TMEV mRNA.