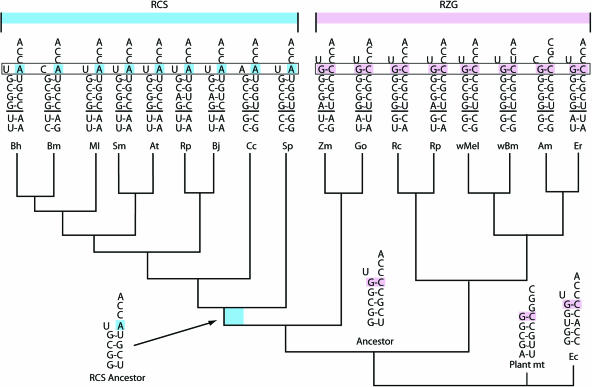
Figure 2.
tRNAHis acceptor stems (with adjacent 5′ leader bases) showing the different identity elements in the α-proteobacteria. The phylogeny is taken from (35,72). Also shown is a parsimony-based reconstruction of ancestral stems and leaders. The most obvious functionally significant differences are outlined in blue for the RCS-clade and in pink for the RZG-clade, to correspond to the covariation of HisRS shown in Figures 3 and 4. Abbreviations are as follows: Bh, Bartonella henselae; Bm, Brucella melitensis; Ml, Mesorhizobium loti; Sm, Sinorhizobium meliloti; At, Agrobacterium tumefaciens; Rp, Rhodopseudomonas palustris; Bj, Bradyrhizobium japonicum; Cc, Caulobacter crescentus; Sp, Silicibacter pomeroyi; Zm, Zymomonas mobilis; Go, Gluconobacter oxydans; Rc, Rickettsia conorii; Rp, Rickettsia prowazekii; wMel, Wolbachia strain wMel; wBm, Wolbachia strain wBm; Am, Anaplasma marginale; Er, Ehrlichia ruminantium.