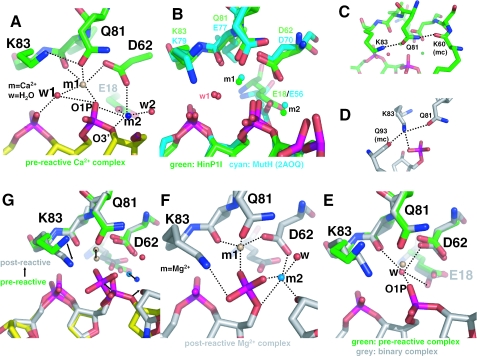
Figure 4.
Two-metal mechanism. (A) In the pre-reactive complex, two Ca2+ ions (m1 and m2) are bound in the active site. The dashed lines indicate hydrogen bonds. (B) Structural superimposition of the active site of HinP1I (green) with that of MutH [cyan; PDB 2AOQ (9)]; both contain the DNA substrate and two Ca2+ ions. (C) In the pre-reactive complex, Q81 (a metal coordinator) interaction with the K83 side chain and the K60 main chain. (D) In the post-reactive complex, K83 links Q81 (a metal coordinator), Q93 (a base recognition residue) and the cleaved phosphate group. (E) In the metal-free binary HinP1I–DNA structure, a water molecule occupies the position near the m1 metal site. (F) In the post-reactive complex, two Mg2+ ions (m1 and m2) are bound in the active site. (G) Superimposition of the pre-reactive and post-reactive complexes, with arrows indicating the movements from pre-reactive to the post-reactive states.