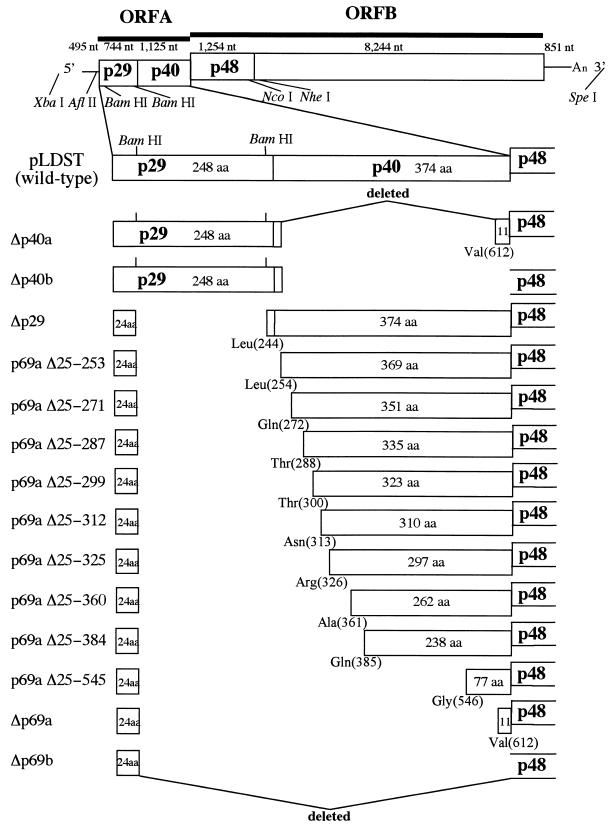
FIG. 1.
Diagram showing the organization of ORF A mutant viruses. The genetic organization of hypovirus CHV1-EP713 is shown at the top. The plus-sense strand of CHV1-EP713 hypovirus dsRNA is 12,712 nucleotides in length, excluding a poly(A) tract, and contains a 495-nucleotide (nt) 5′ noncoding leader sequence, two contiguous ORFs (1,869-nucleotide ORF A and 9,498-nucleotide ORF B) and an 851-nucleotide 3′ noncoding region. ORF A encodes a 69-kDa polyprotein (p69) that is autocatalytically processed into p29 and p40 by the action of a papain-like cysteine protease domain located within the p29 coding region. Key restriction enzyme recognition sites within the full-length CHV1-EP713 infectious cDNA clone, pLDST (9), used for mutant viral cDNA constructions included AflII (CHV1-EP713 map position 450 [28]), BamHI (CHV1-EP713 map positions 562 and 1219), PstI (CHV1-EP713 map position 1846), NcoI (CHV1-EP713 map position 3263), NheI (CHV1-EP713 map position 3705), SpeI (vector sequence), and XbaI (vector sequence). ORF A deletion mutant viruses are shown below the wild-type virus cDNA. Δp40a and Δp40b lack 96.5 and 99.5% of the p40 coding sequence within the context of di- and monocistronic genome organizations, respectively. For Δp40a, two BglII-derived amino acid residues (aspartic acid and proline) were added during the cloning procedure downstream of p40 Arg(2) and fused with p40 Val(612), while the added proline is fused with Met(1) of p48 encoded by ORF B in Δp40b. Δp29, described earlier (11), has a deletion of 87.5% of the p29 gene while retaining the N-terminal 24 codons necessary for virus viability (32). Extreme mutants Δp69a and Δp69b contained 94.4 and 96.1% deletions of the ORF A sequence, again, within the context of the di- and monocistronic genome organizations described for Δp40a and Δp40b, respectively. p29 residue Pro(24) is fused with p40 Val(612) for Δp69a or with p48 Met(1) for Δp69b. A series of nine mutants containing progressive extensions from p40 Val(612) towards the p40 N terminus Leu(254) are presented between Δp69a and Δp29. These extension mutant viruses were used in transfection (gain-of-function) assays to map the region of the p40 coding domain responsible for suppression of pustule formation.