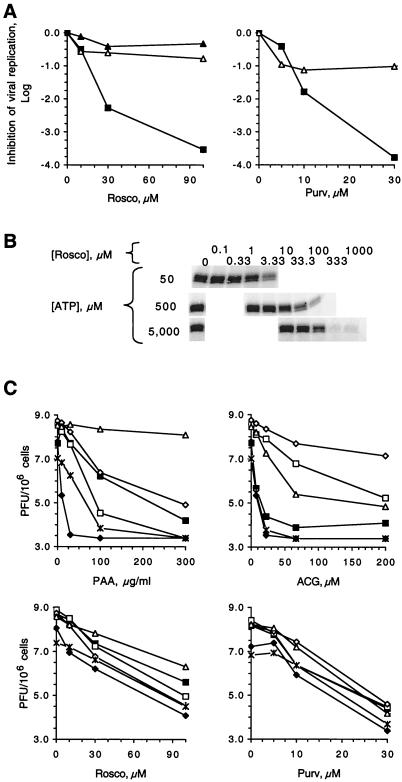
FIG. 1.
Rosco and Purv inhibit wild-type and drug-resistant strains of HSV-1 and -2, but not vaccinia virus or LCMV. (A) Vero cells infected with HSV-1, vaccinia virus, or LCMV were treated with increasing concentrations of Rosco or Purv. Inhibition of viral replication at 20 h postinfection, expressed as the log, is plotted against concentration of drug. ▵, vaccinia virus; ▴, LCMV; ▪, HSV-1. (B) Inhibition of cdk2/cyclinA phosphorylation of histone H1 by Rosco was evaluated in the presence of increasing concentrations of ATP, as indicated on the left of each gel. Kinase reactions were performed in vitro, phosphorylated histone H1 was then resolved by sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis, and gels were dried and exposed on a PhosphorImager. (C) Vero cells were infected with wild-type HSV-1 (KOS), wild-type HSV-2 (strain 186 or 333), or drug-resistant HSV-1 mutants (ACGr5, dlPstTK−, and PAAr5). Infected cells were treated with the indicated concentrations (on x axes) of PAA, ACG, Rosco, or Purv. Viral titers at 20 h postinfection were plotted against drug concentration. ▪, HSV-1 KOS; □, HSV-1 ACGr5; ⋄, HSV-1 dlPstTK−; ▵, HSV-1 PAAr5; ×, HSV-2 strain 333; ♦, HSV-2 strain 186.