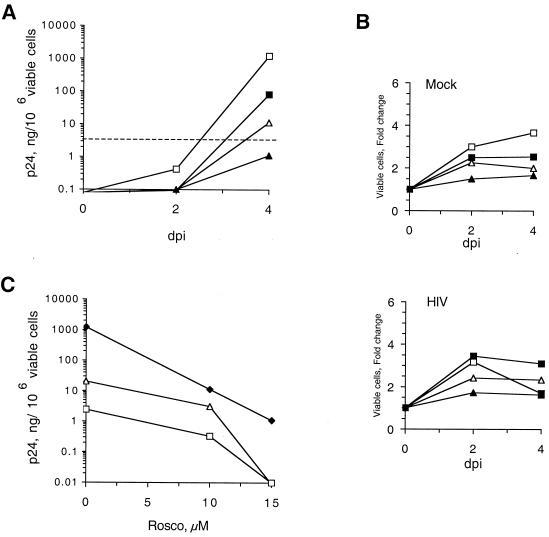
FIG. 3.
Rosco inhibits replication of wild-type and drug-resistant strains of HIV-1 and enhances survival of cells in infected cultures. (A) CEMx174 cells were infected with HIV-1 and treated with Rosco. Levels of p24 at 2 and 4 days postinfection (dpi), expressed as picograms of p24 per 106 viable cells, are plotted against drug concentration. The level of inoculum is indicated by the dashed line. Symbols for Rosco concentrations: □, 0 μM; ▪, 5 μM; ▵, 10 μM; ▴, 15 μM. (B) Mock- or HIV-1-infected cells were treated with Rosco and counted at 2 and 4 dpi. The fold change in the number of viable cells is plotted against days postinfection for each concentration of drug. Symbols for Rosco concentration are as described for panel A. (C) CEMx174 cells were infected with PI- or RTI-resistant HIV-1 strain L10R/M46I/L63P/V82T/I84V (13) or RTMDR/MT-2 (35), respectively. Infected cells were treated with Rosco and levels of p24 per 106 viable cells on day 4 pi are plotted against Rosco concentrations. ♦, wild type; □, PIr; ▵, RTIr. The levels of p24 produced by wild-type HIV-1 on day 4 pi in the presence of Rosco (see Fig. 4A) are included for comparison.