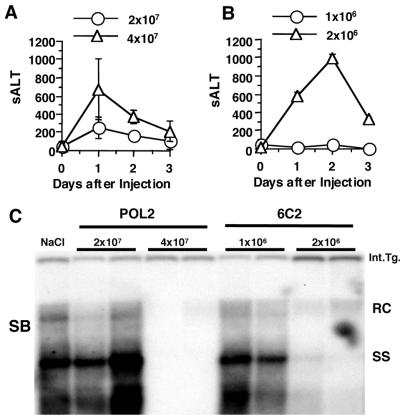
FIG. 8.
Minimum number of CTLs that is necessary to inhibit HBV replication. POL2 CTL clones (2 × 107 or 4 × 107) (A) or 6C2 CTL clones (1 × 106 or 2 × 106) (B) were adoptively transferred to HBV transgenic mice (three mice per group) to examine their ability to cause hepatitis and to control HBV replication in vivo. sALT activity (mean ± SD) at each time point is expressed in units/liter. (C) Total hepatic DNA from the HBV transgenic recipients of the POL (POL2)- and ENV (6C2)-specific CTL clones was analyzed for HBV DNA by Southern blotting (SB). The results for two representative animals per group are shown. All DNA samples were RNase treated before quantitation and gel electrophoresis. Bands corresponding to the integrated transgene (Int.Tg.), RC strain double-stranded HBV DNA, and SS strain linear HBV DNA replicative forms are indicated. The integrated transgene can be used to normalize the amount of DNA bound to the membrane. The filter was hybridized with a 32P-labeled HBV-specific DNA probe. Results were compared with those observed in livers pooled from 10 age-, sex-, and serum HBeAg-matched saline-injected transgenic controls (NaCl).