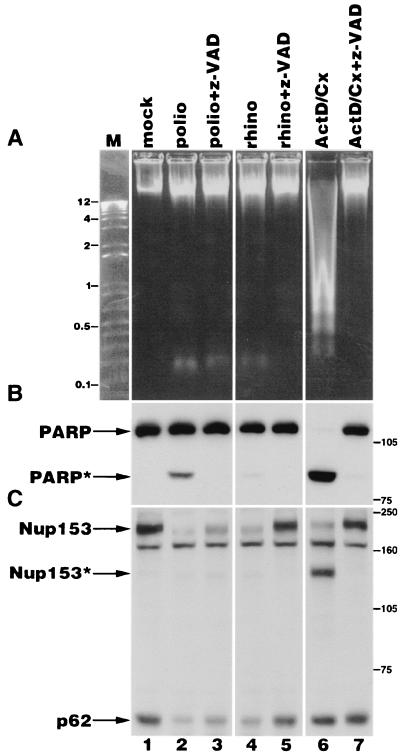
FIG. 7.
Analysis of Nup153 and p62 in apoptotic and picornavirus-infected cells. (A) Electrophoresis of genomic DNA isolated from HeLa cells following various treatments. mock, lysate from mock-infected cells; polio, lysates from cells that have been infected with poliovirus for 5 h; rhino, lysates from cells that have been infected with rhinovirus for 6 h; ActD/Cx, lysates from cells that have been treated with actinomycin D and cycloheximide for 6 h; z-VAD, z-VAD-fmk added immediately following virus adsorption or coincident with the addition of actinomycin D and cycloheximide; M, molecular size markers (kilobases). (B) Fifty micrograms of whole-cell lysates prepared from cells treated as described in panel A was analyzed by immunoblotting to detect PARP. The positions of the full-length and cleaved forms of PARP are indicated by PARP and PARP∗, respectively. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated. (C) Fifty micrograms of whole-cell lysates was analyzed by immunoblotting with monoclonal antibody 414 to detect Nup153 and p62. The positions of the full-length and cleaved forms of Nup153 are indicated by Nup153 and Nup153∗, respectively. The positions of molecular mass markers (in kilodaltons) are indicated.