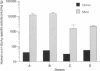Abstract
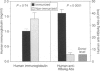
An approach to develop fully human monoclonal antibodies in a human/mouse radiation chimera, the Trimera system, is described. In this system, functional human lymphocytes are engrafted in normal strains of mice which are rendered immuno-incompetent by lethal total body irradiation followed by radioprotection with severe combined immunodeficient (SCID) mouse bone marrow. Following transplantation, human lymphocytes colonize murine lymphatic organs and secrete human immunoglobulins. We have established this system as a tool to develop fully human monoclonal antibodies, and applied it for the generation of monoclonal antibodies specific for hepatitis B virus surface antigen. A strong memory response to hepatitis B surface antigen was elicited in Trimera engrafted with lymphocytes from human donors positive for antibodies to hepatitis B surface antigen. The human specific antibody fraction in the Trimera was 10(2)-10(3)-fold higher as compared with that found in the donors. Spleens were harvested from Trimera mice showing high specific-antibody titres and cells were fused to a human-mouse heteromyeloma fusion partner. Several stable hybridoma clones were isolated and characterized. These hybridomas produce high-affinity, IgG, anti-hepatitis B surface antigen antibodies demonstrating the potential of the Trimera system for generating fully human monoclonal antibodies. The biological function and the neutralizing activity of these antibodies are currently being tested.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barbas C. F., 3rd, Kang A. S., Lerner R. A., Benkovic S. J. Assembly of combinatorial antibody libraries on phage surfaces: the gene III site. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7978–7982. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7978. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brüggemann M., Neuberger M. S. Strategies for expressing human antibody repertoires in transgenic mice. Immunol Today. 1996 Aug;17(8):391–397. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)10025-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burakova T., Marcus H., Canaan A., Dekel B., Shezen E., David M., Lubin I., Segal H., Yair R. Engrafted human T and B lymphocytes form mixed follicles in lymphoid organs of human/mouse and human/rat radiation chimera. Transplantation. 1997 Apr 27;63(8):1166–1171. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199704270-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlsson R., Mårtensson C., Kalliomäki S., Ohlin M., Borrebaeck C. A. Human peripheral blood lymphocytes transplanted into SCID mice constitute an in vivo culture system exhibiting several parameters found in a normal humoral immune response and are a source of immunocytes for the production of human monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1992 Feb 15;148(4):1065–1071. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deinhardt F., Zuckerman A. J. Immunization against hepatitis B: report on a WHO meeting on viral hepatitis in Europe. J Med Virol. 1985 Nov;17(3):209–217. doi: 10.1002/jmv.1890170302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ehrlich P. H., Moustafa Z. A., Justice J. C., Harfeldt K. E., Kelley R. L., Ostberg L. Characterization of human monoclonal antibodies directed against hepatitis B surface antigen. Hum Antibodies Hybridomas. 1992 Jan;3(1):2–7. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friguet B., Chaffotte A. F., Djavadi-Ohaniance L., Goldberg M. E. Measurements of the true affinity constant in solution of antigen-antibody complexes by enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Mar 18;77(2):305–319. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90044-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia S., Dadaglio G., Gougeon M. L. Limits of the human-PBL-SCID mice model: severe restriction of the V beta T-cell repertoire of engrafted human T cells. Blood. 1997 Jan 1;89(1):329–336. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichimori Y., Sasano K., Itoh H., Hitotsumachi S., Kimura Y., Kaneko K., Kida M., Tsukamoto K. Establishment of hybridomas secreting human monoclonal antibodies against tetanus toxin and hepatitis B virus surface antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):26–33. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91397-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ifversen P., Borrebaeck C. A. SCID-hu-PBL: a model for making human antibodies? Semin Immunol. 1996 Aug;8(4):243–248. doi: 10.1006/smim.1996.0030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane R. D., Crissman R. S., Ginn S. High efficiency fusion procedure for producing monoclonal antibodies against weak immunogens. Methods Enzymol. 1986;121:183–192. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(86)21017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levite M., Meshorer A., Reisner Y. A rapid method for obtaining murine bone marrow cells in high yield. Bone Marrow Transplant. 1991 Sep;8(3):225–227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lonberg N., Taylor L. D., Harding F. A., Trounstine M., Higgins K. M., Schramm S. R., Kuo C. C., Mashayekh R., Wymore K., McCabe J. G. Antigen-specific human antibodies from mice comprising four distinct genetic modifications. Nature. 1994 Apr 28;368(6474):856–859. doi: 10.1038/368856a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin I., Faktorowich Y., Lapidot T., Gan Y., Eshhar Z., Gazit E., Levite M., Reisner Y. Engraftment and development of human T and B cells in mice after bone marrow transplantation. Science. 1991 Apr 19;252(5004):427–431. doi: 10.1126/science.1826797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin I., Segall H., Erlich P., David M., Marcus H., Fire G., Burakova T., Kulova L., Reisner Y. Conversion of normal rats into SCID-like animals by means of bone marrow transplantation from SCID donors allows engraftment of human peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Transplantation. 1995 Oct 15;60(7):740–747. doi: 10.1097/00007890-199510150-00022. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lubin I., Segall H., Marcus H., David M., Kulova L., Steinitz M., Erlich P., Gan J., Reisner Y. Engraftment of human peripheral blood lymphocytes in normal strains of mice. Blood. 1994 Apr 15;83(8):2368–2381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcus H., David M., Canaan A., Kulova L., Lubin I., Segall H., Denes L., Erlich P., Galun E., Gan J. Human/mouse radiation chimera are capable of mounting a human primary humoral response. Blood. 1995 Jul 1;86(1):398–406. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCafferty J., Griffiths A. D., Winter G., Chiswell D. J. Phage antibodies: filamentous phage displaying antibody variable domains. Nature. 1990 Dec 6;348(6301):552–554. doi: 10.1038/348552a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McMahon G., Ehrlich P. H., Moustafa Z. A., McCarthy L. A., Dottavio D., Tolpin M. D., Nadler P. I., Ostberg L. Genetic alterations in the gene encoding the major HBsAg: DNA and immunological analysis of recurrent HBsAg derived from monoclonal antibody-treated liver transplant patients. Hepatology. 1992 May;15(5):757–766. doi: 10.1002/hep.1840150503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Milstein C. The Croonian lecture, 1989. Antibodies: a paradigm for the biology of molecular recognition. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1990 Feb 22;239(1294):1–16. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1990.0006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mosier D. E. Adoptive transfer of human lymphoid cells to severely immunodeficient mice: models for normal human immune function, autoimmunity, lymphomagenesis, and AIDS. Adv Immunol. 1991;50:303–325. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60828-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Schneider W. P., Selick H. E., Payne P. W., Landolfi N. F., Duncan J. F., Avdalovic N. M., Levitt M., Junghans R. P., Waldmann T. A. A humanized antibody that binds to the interleukin 2 receptor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1989 Dec;86(24):10029–10033. doi: 10.1073/pnas.86.24.10029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Randen I., Thompson K. M., Thorpe S. J., Førre O., Natvig J. B. Human monoclonal IgG rheumatoid factors from the synovial tissue of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Immunol. 1993 Jun;37(6):668–672. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3083.1993.tb01681.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandhu J., Shpitz B., Gallinger S., Hozumi N. Human primary immune response in SCID mice engrafted with human peripheral blood lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1994 Apr 15;152(8):3806–3813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawada H., Iwasa S., Nishimura O., Kitano K. Efficient production of anti-(hepatitis B virus) antibodies and their neutralizing activity in chimpanzees. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol. 1995 Jul;43(3):445–451. doi: 10.1007/BF00218447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saxon A., Macy E., Denis K., Tary-Lehmann M., Witte O., Braun J. Limited B cell repertoire in severe combined immunodeficient mice engrafted with peripheral blood mononuclear cells derived from immunodeficient or normal humans. J Clin Invest. 1991 Feb;87(2):658–665. doi: 10.1172/JCI115043. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Segall H., Lubin I., Marcus H., Canaan A., Reisner Y. Generation of primary antigen-specific human cytotoxic T lymphocytes in human/mouse radiation chimera. Blood. 1996 Jul 15;88(2):721–730. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shouval D., Ilan Y., Adler R., Deepen R., Panet A., Even-Chen Z., Gorecki M., Gerlich W. H. Improved immunogenicity in mice of a mammalian cell-derived recombinant hepatitis B vaccine containing pre-S1 and pre-S2 antigens as compared with conventional yeast-derived vaccines. Vaccine. 1994 Nov;12(15):1453–1459. doi: 10.1016/0264-410x(94)90155-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steinitz M., Klein G., Koskimies S., Makel O. EB virus-induced B lymphocyte cell lines producing specific antibody. Nature. 1977 Sep 29;269(5627):420–422. doi: 10.1038/269420a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tary-Lehmann M., Saxon A. Human mature T cells that are anergic in vivo prevail in SCID mice reconstituted with human peripheral blood. J Exp Med. 1992 Feb 1;175(2):503–516. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.2.503. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson K., Barden G., Sutherland J., Beldon I., Melamed M. Human monoclonal antibodies to C, c, E, e and G antigens of the Rh system. Immunology. 1990 Nov;71(3):323–327. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter G., Milstein C. Man-made antibodies. Nature. 1991 Jan 24;349(6307):293–299. doi: 10.1038/349293a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]