Abstract
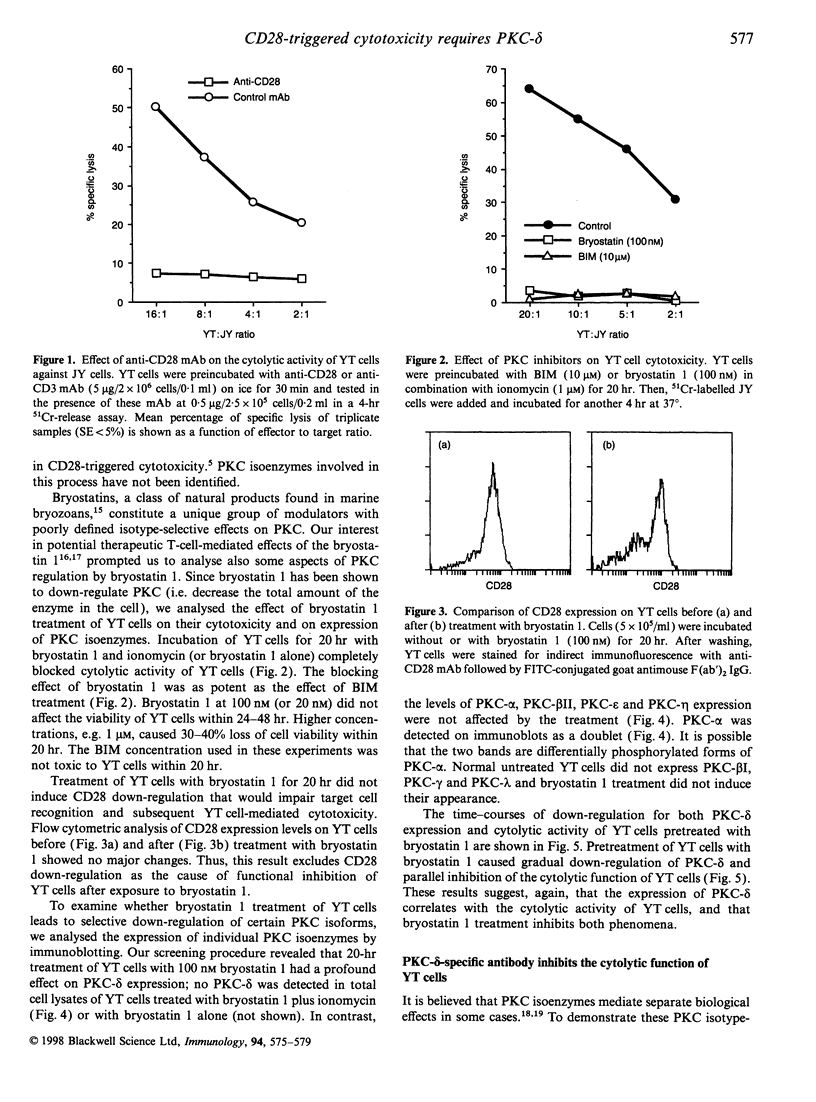
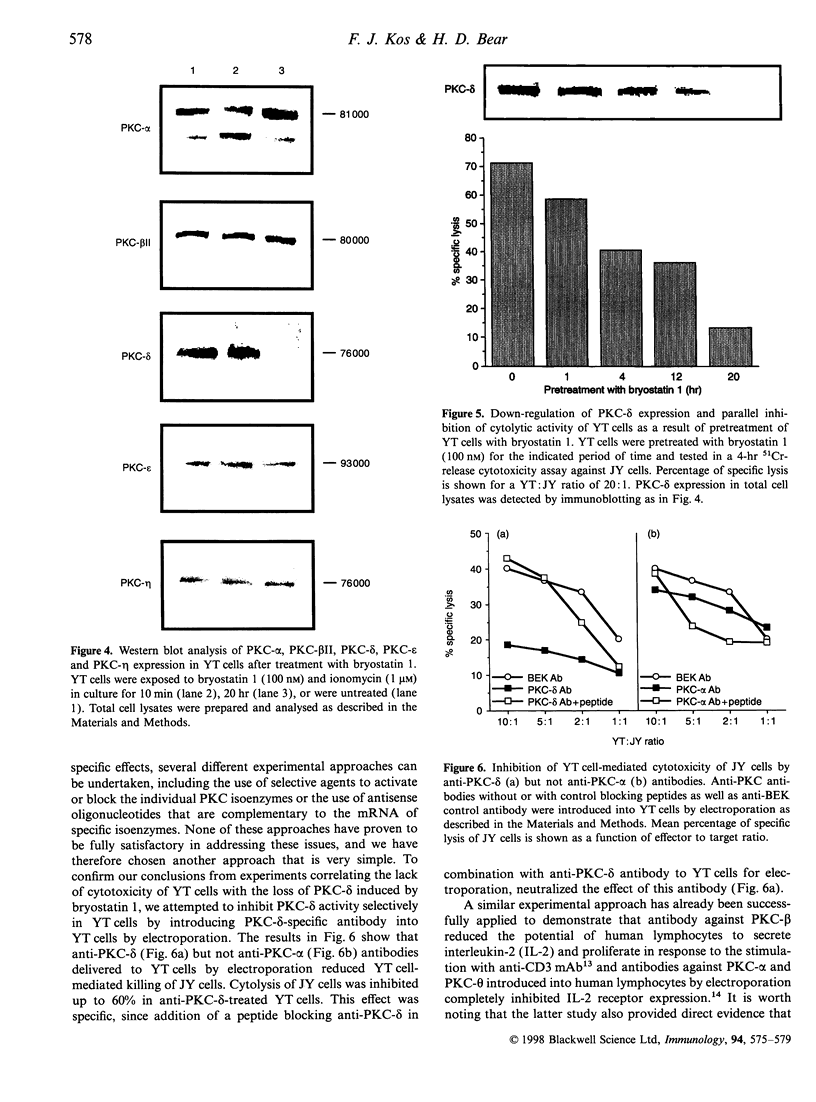
Ligation of CD28 molecules expressed on the surface of human leukaemic natural killer-like YT cells triggers intracellular signals leading to cytolysis of target cells expressing CD80 or CD86 molecules. Known intracellular events include tyrosine phosphorylation, activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and protein kinase C (PKC). In this study, we report that PKC-delta isoenzyme activity is required for CD28-triggered cytotoxicity mediated by YT cells and we also demonstrate that one of the primary targets of bryostatin 1, a modulator of PKC activity, is PKC-delta. Treatment of YT cells with bryostatin 1 caused degradation of PKC-delta, but not other PKC isoenzymes, and completely blocked the cytolytic activity of YT cells. In addition, PKC-delta-specific antibody introduced into YT cells by electroporation inhibited partially the YT cell-mediated cytotoxicity of B-lymphoblastoid cell line JY. This effect was specific, since addition of anti-PKC-delta antibody-blocking peptide in combination with anti-PKC-delta antibody to YT cells for electroporation, neutralized the effect of this antibody. These results demonstrate that YT cell cytolytic activity is dependent on PKC-delta, which is selectively down-regulated by bryostatin 1.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Azuma M., Cayabyab M., Buck D., Phillips J. H., Lanier L. L. Involvement of CD28 in MHC-unrestricted cytotoxicity mediated by a human natural killer leukemia cell line. J Immunol. 1992 Aug 15;149(4):1115–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dekker L. V., Parker P. J. Protein kinase C--a question of specificity. Trends Biochem Sci. 1994 Feb;19(2):73–77. doi: 10.1016/0968-0004(94)90038-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaaz S., Baetz K., Olsen K., Podack E., Griffiths G. M. Serial killing by cytotoxic T lymphocytes: T cell receptor triggers degranulation, re-filling of the lytic granules and secretion of lytic proteins via a non-granule pathway. Eur J Immunol. 1995 Apr;25(4):1071–1079. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830250432. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapeller R., Cantley L. C. Phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase. Bioessays. 1994 Aug;16(8):565–576. doi: 10.1002/bies.950160810. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kos F. J., Engleman E. G. Requirement for natural killer cells in the induction of cytotoxic T cells. J Immunol. 1995 Jul 15;155(2):578–584. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kos F. J., Müllbacher A. IL-2-independent activity of IL-7 in the generation of secondary antigen-specific cytotoxic T cell responses in vitro. J Immunol. 1993 Jan 15;150(2):387–393. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lu Y., Rodriguez R., Bjorndahl J., Phillips C. A., Trevillyan J. M. CD28-dependent killing by human YT cells requires phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Eur J Immunol. 1996 Jun;26(6):1278–1284. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830260615. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakanishi H., Brewer K. A., Exton J. H. Activation of the zeta isozyme of protein kinase C by phosphatidylinositol 3,4,5-trisphosphate. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 5;268(1):13–16. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ozawa K., Szallasi Z., Kazanietz M. G., Blumberg P. M., Mischak H., Mushinski J. F., Beaven M. A. Ca(2+)-dependent and Ca(2+)-independent isozymes of protein kinase C mediate exocytosis in antigen-stimulated rat basophilic RBL-2H3 cells. Reconstitution of secretory responses with Ca2+ and purified isozymes in washed permeabilized cells. J Biol Chem. 1993 Jan 25;268(3):1749–1756. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rudd C. E. Upstream-downstream: CD28 cosignaling pathways and T cell function. Immunity. 1996 Jun;4(6):527–534. doi: 10.1016/s1074-7613(00)80479-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szamel M., Appel A., Schwinzer R., Resch K. Different protein kinase C isoenzymes regulate IL-2 receptor expression or IL-2 synthesis in human lymphocytes stimulated via the TCR. J Immunol. 1998 Mar 1;160(5):2207–2214. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szamel M., Bartels F., Resch K. Cyclosporin A inhibits T cell receptor-induced interleukin-2 synthesis of human T lymphocytes by selectively preventing a transmembrane signal transduction pathway leading to sustained activation of a protein kinase C isoenzyme, protein kinase C-beta. Eur J Immunol. 1993 Dec;23(12):3072–3081. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830231205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szamel M., Resch K. T-cell antigen receptor-induced signal-transduction pathways--activation and function of protein kinases C in T lymphocytes. Eur J Biochem. 1995 Feb 15;228(1):1–15. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1995.tb20221.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Teng J. M., Liu X. R., Mills G. B., Dupont B. CD28-mediated cytotoxicity by the human leukemic NK cell line YT involves tyrosine phosphorylation, activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase, and protein kinase C. J Immunol. 1996 May 1;156(9):3222–3232. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle T. M., Inge T. H., Bethke K. P., McCrady C. W., Pettit G. R., Bear H. D. Activation and growth of murine tumor-specific T-cells which have in vivo activity with bryostatin 1. Cancer Res. 1992 Feb 1;52(3):548–553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tuttle T. M., Inge T. H., Wirt C. P., Frank J. L., McCrady C. M., Bear H. D. Bryostatin 1 activates T cells that have antitumor activity. J Immunother (1991) 1992 Aug;12(2):75–81. doi: 10.1097/00002371-199208000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward S. G., June C. H., Olive D. PI 3-kinase: a pivotal pathway in T-cell activation? Immunol Today. 1996 Apr;17(4):187–197. doi: 10.1016/0167-5699(96)80618-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilkinson S. E., Hallam T. J. Protein kinase C: is its pivotal role in cellular activation over-stated? Trends Pharmacol Sci. 1994 Feb;15(2):53–57. doi: 10.1016/0165-6147(94)90110-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yodoi J., Teshigawara K., Nikaido T., Fukui K., Noma T., Honjo T., Takigawa M., Sasaki M., Minato N., Tsudo M. TCGF (IL 2)-receptor inducing factor(s). I. Regulation of IL 2 receptor on a natural killer-like cell line (YT cells). J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1623–1630. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


