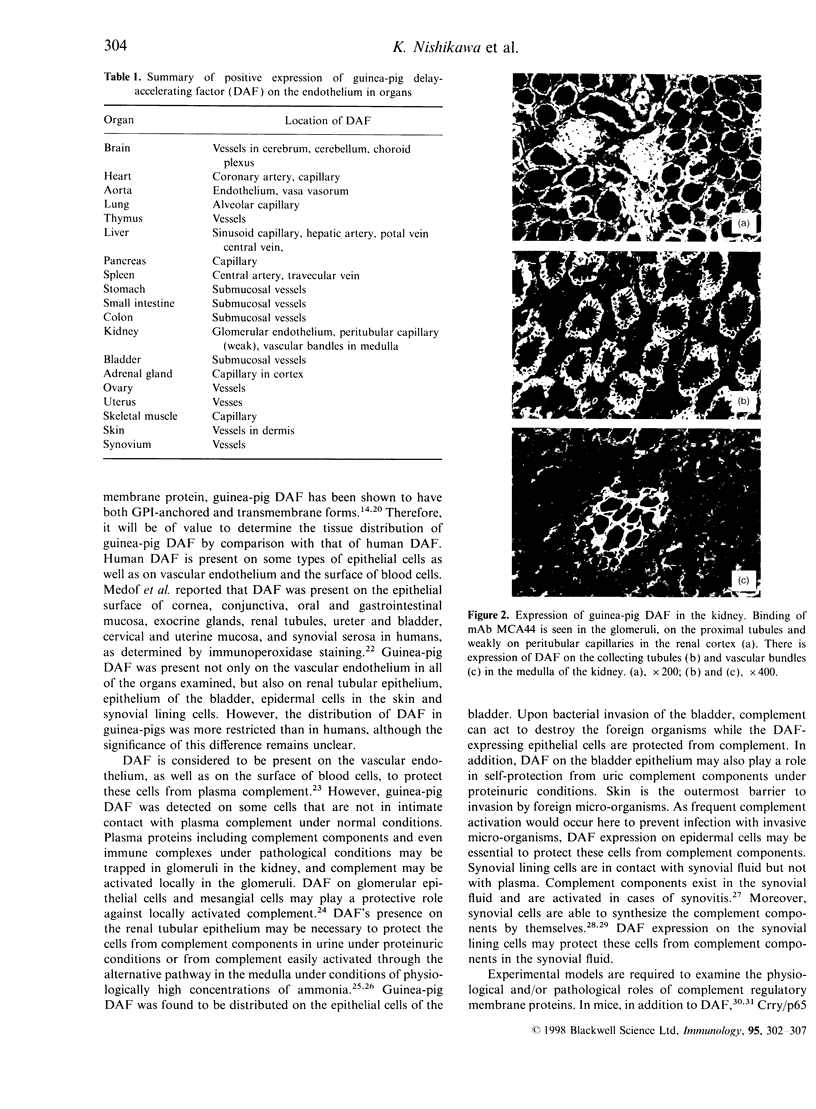
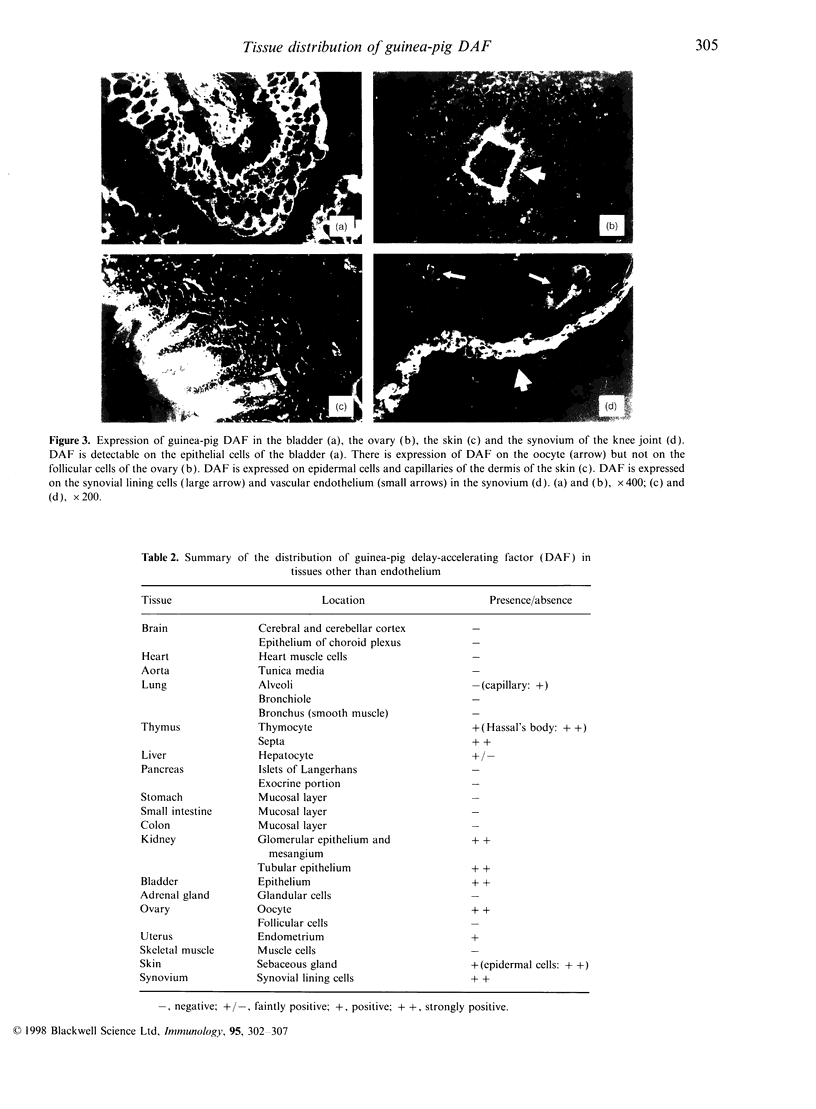
Abstract
MCA44 is a monoclonal antibody (mAb) to guinea-pig decay-accelerating factor (DAF) and, using this mAb, tissue distribution of guinea-pig DAF was studied by immunofluorescence. Guinea-pig DAF was found to be expressed not only on the vascular endothelium but also on different types of cells, such as the tubular epithelium of the kidney, epidermal cells of the skin and synovial lining cells. As there was no significant reduction in staining intensity with MCA44 following treatment with phosphatidylinositol-specific phospholipase C, many guinea-pig DAF molecules expressed in these tissues may be of the transmembrane form.
Full text
PDF
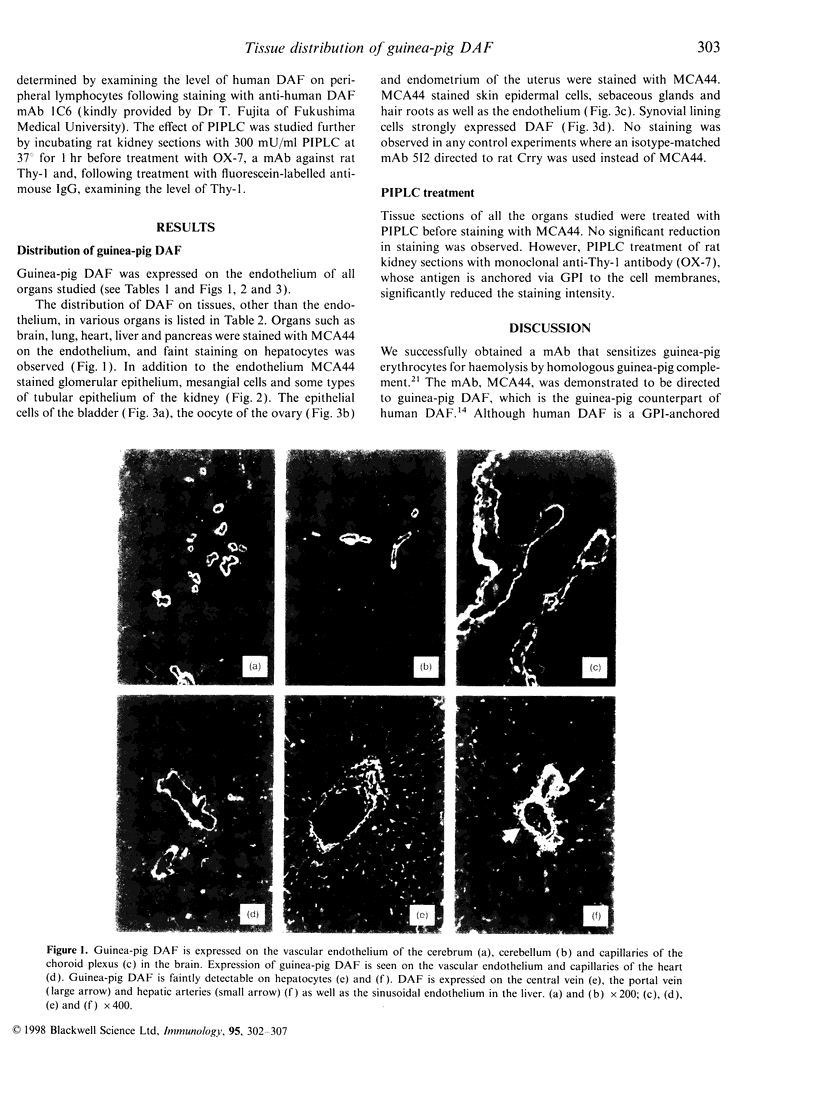


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Abbink J. J., Kamp A. M., Nuijens J. H., Erenberg A. J., Swaak A. J., Hack C. E. Relative contribution of contact and complement activation to inflammatory reactions in arthritic joints. Ann Rheum Dis. 1992 Oct;51(10):1123–1128. doi: 10.1136/ard.51.10.1123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cole J. L., Housley G. A., Jr, Dykman T. R., MacDermott R. P., Atkinson J. P. Identification of an additional class of C3-binding membrane proteins of human peripheral blood leukocytes and cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):859–863. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.859. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies A., Simmons D. L., Hale G., Harrison R. A., Tighe H., Lachmann P. J., Waldmann H. CD59, an LY-6-like protein expressed in human lymphoid cells, regulates the action of the complement membrane attack complex on homologous cells. J Exp Med. 1989 Sep 1;170(3):637–654. doi: 10.1084/jem.170.3.637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Funabashi K., Okada N., Matsuo S., Yamamoto T., Morgan B. P., Okada H. Tissue distribution of complement regulatory membrane proteins in rats. Immunology. 1994 Mar;81(3):444–451. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harada R., Okada N., Fujita T., Okada H. Purification of 1F5 antigen that prevents complement attack on homologous cell membranes. J Immunol. 1990 Mar 1;144(5):1823–1828. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka Y., Yuzawa Y., Nishikawa K., Fukatsu A., Okada N., Okada H., Mizuno M., Matsuo S. Role of a rat membrane inhibitor of complement in anti-basement membrane antibody-induced renal injury. Kidney Int. 1995 Dec;48(6):1728–1737. doi: 10.1038/ki.1995.471. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holguin M. H., Fredrick L. R., Bernshaw N. J., Wilcox L. A., Parker C. J. Isolation and characterization of a membrane protein from normal human erythrocytes that inhibits reactive lysis of the erythrocytes of paroxysmal nocturnal hemoglobinuria. J Clin Invest. 1989 Jul;84(1):7–17. doi: 10.1172/JCI114172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hostetter M. K. The third component of complement: new functions for an old friend. J Lab Clin Med. 1993 Nov;122(5):491–496. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ichida S., Yuzawa Y., Okada H., Yoshioka K., Matsuo S. Localization of the complement regulatory proteins in the normal human kidney. Kidney Int. 1994 Jul;46(1):89–96. doi: 10.1038/ki.1994.247. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kameyoshi Y., Matsushita M., Okada H. Murine membrane inhibitor of complement which accelerates decay of human C3 convertase. Immunology. 1989 Dec;68(4):439–444. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kim Y. U., Kinoshita T., Molina H., Hourcade D., Seya T., Wagner L. M., Holers V. M. Mouse complement regulatory protein Crry/p65 uses the specific mechanisms of both human decay-accelerating factor and membrane cofactor protein. J Exp Med. 1995 Jan 1;181(1):151–159. doi: 10.1084/jem.181.1.151. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lublin D. M., Atkinson J. P. Decay-accelerating factor: biochemistry, molecular biology, and function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1989;7:35–58. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.07.040189.000343. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matsuo S., Ichida S., Takizawa H., Okada N., Baranyi L., Iguchi A., Morgan B. P., Okada H. In vivo effects of monoclonal antibodies that functionally inhibit complement regulatory proteins in rats. J Exp Med. 1994 Nov 1;180(5):1619–1627. doi: 10.1084/jem.180.5.1619. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Kinoshita T., Nussenzweig V. Inhibition of complement activation on the surface of cells after incorporation of decay-accelerating factor (DAF) into their membranes. J Exp Med. 1984 Nov 1;160(5):1558–1578. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.5.1558. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Medof M. E., Walter E. I., Rutgers J. L., Knowles D. M., Nussenzweig V. Identification of the complement decay-accelerating factor (DAF) on epithelium and glandular cells and in body fluids. J Exp Med. 1987 Mar 1;165(3):848–864. doi: 10.1084/jem.165.3.848. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molina H., Wong W., Kinoshita T., Brenner C., Foley S., Holers V. M. Distinct receptor and regulatory properties of recombinant mouse complement receptor 1 (CR1) and Crry, the two genetic homologues of human CR1. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):121–129. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.121. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nath K. A., Hostetter M. K., Hostetter T. H. Pathophysiology of chronic tubulo-interstitial disease in rats. Interactions of dietary acid load, ammonia, and complement component C3. J Clin Invest. 1985 Aug;76(2):667–675. doi: 10.1172/JCI112020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson-Weller A., Burge J., Fearon D. T., Weller P. F., Austen K. F. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane glycoprotein with decay-accelerating activity for C3 convertases of the complement system. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):184–189. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikage H., Baranyi L., Okada H., Okada N., Isobe K., Nomura A., Yoshida F., Matsuo S. The role of a complement regulatory protein in rat mesangial glomerulonephritis. J Am Soc Nephrol. 1995 Aug;6(2):234–241. doi: 10.1681/ASN.V62234. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishikawa K., Matsuo S., Okada N., Morgan B. P., Okada H. Local inflammation caused by a monoclonal antibody that blocks the function of the rat membrane inhibitor of C3 convertase. J Immunol. 1996 Feb 1;156(3):1182–1188. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomura A., Nishikawa K., Yuzawa Y., Okada H., Okada N., Morgan B. P., Piddlesden S. J., Nadai M., Hasegawa T., Matsuo S. Tubulointerstitial injury induced in rats by a monoclonal antibody that inhibits function of a membrane inhibitor of complement. J Clin Invest. 1995 Nov;96(5):2348–2356. doi: 10.1172/JCI118291. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Miwa T., Okada N., Nonaka M., Okada H. Multiple isoforms of guinea pig decay-accelerating factor (DAF) generated by alternative splicing. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 15;155(6):3037–3048. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Harada R., Fujita T., Okada H. A novel membrane glycoprotein capable of inhibiting membrane attack by homologous complement. Int Immunol. 1989;1(2):205–208. doi: 10.1093/intimm/1.2.205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Harada R., Fujita T., Okada H. Monoclonal antibodies capable of causing hemolysis of neuraminidase-treated human erythrocytes by homologous complement. J Immunol. 1989 Oct 1;143(7):2262–2266. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okada N., Tanaka H., Takizawa H., Okada H. A monoclonal antibody that blocks the complement regulatory activity of guinea pig erythrocytes and characterization of the antigen involved as guinea pig decay-accelerating factor. J Immunol. 1995 Jun 1;154(11):6103–6111. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddy S., Colten H. R. Rheumatoid arthritis. Biosynthesis of complement proteins by synovial tissues. N Engl J Med. 1974 Jun 6;290(23):1284–1288. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197406062902304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sakurada C., Seno H., Dohi N., Takizawa H., Nonaka M., Okada N., Okada H. Molecular cloning of the rat complement regulatory protein, 5I2 antigen. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1994 Feb 15;198(3):819–826. doi: 10.1006/bbrc.1994.1117. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schönermark S., Rauterberg E. W., Shin M. L., Löke S., Roelcke D., Hänsch G. M. Homologous species restriction in lysis of human erythrocytes: a membrane-derived protein with C8-binding capacity functions as an inhibitor. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1772–1776. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spicer A. P., Seldin M. F., Gendler S. J. Molecular cloning and chromosomal localization of the mouse decay-accelerating factor genes. Duplicated genes encode glycosylphosphatidylinositol-anchored and transmembrane forms. J Immunol. 1995 Sep 15;155(6):3079–3091. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takizawa H., Okada N., Okada H. Complement inhibitor of rat cell membrane resembling mouse Crry/p65. J Immunol. 1994 Mar 15;152(6):3032–3038. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang G., Nonaka M., He C., Okada N., Nakashima I., Okada H. Functional differences among multiple isoforms of guinea pig decay-accelerating factor. J Immunol. 1998 Mar 15;160(6):3014–3022. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zalman L. S., Wood L. M., Müller-Eberhard H. J. Isolation of a human erythrocyte membrane protein capable of inhibiting expression of homologous complement transmembrane channels. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1986 Sep;83(18):6975–6979. doi: 10.1073/pnas.83.18.6975. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]