Abstract
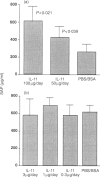
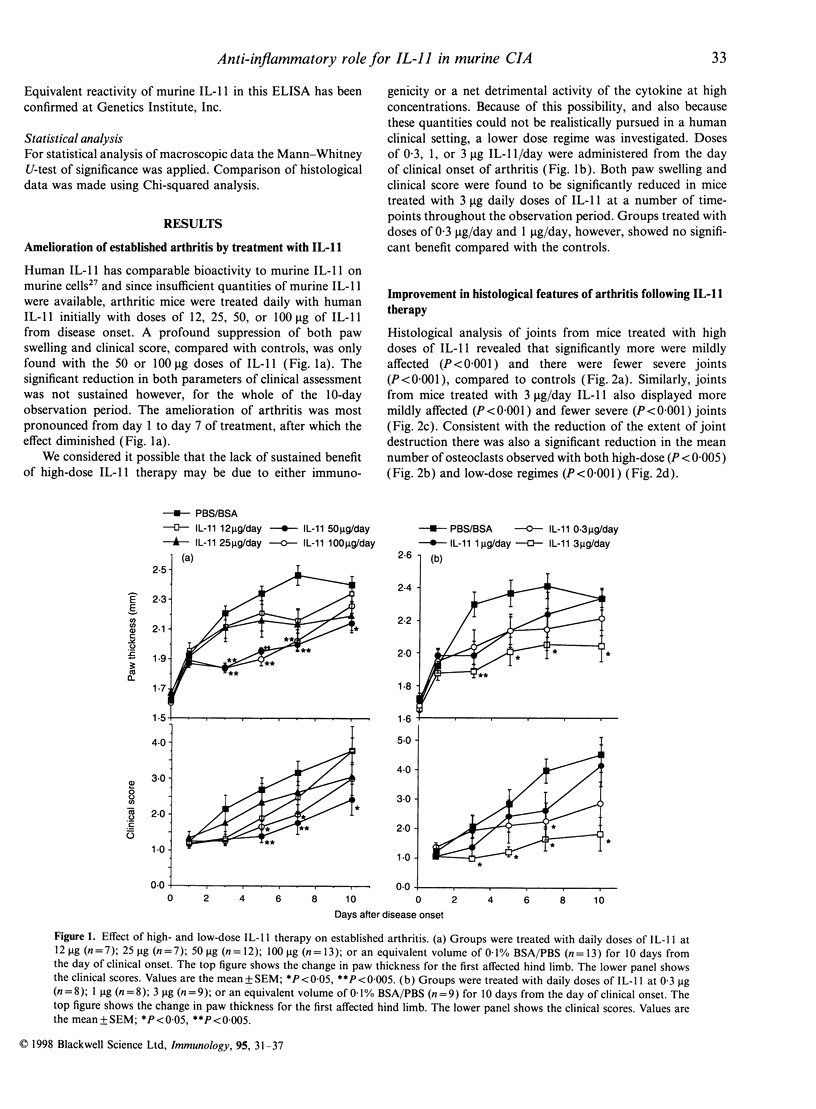
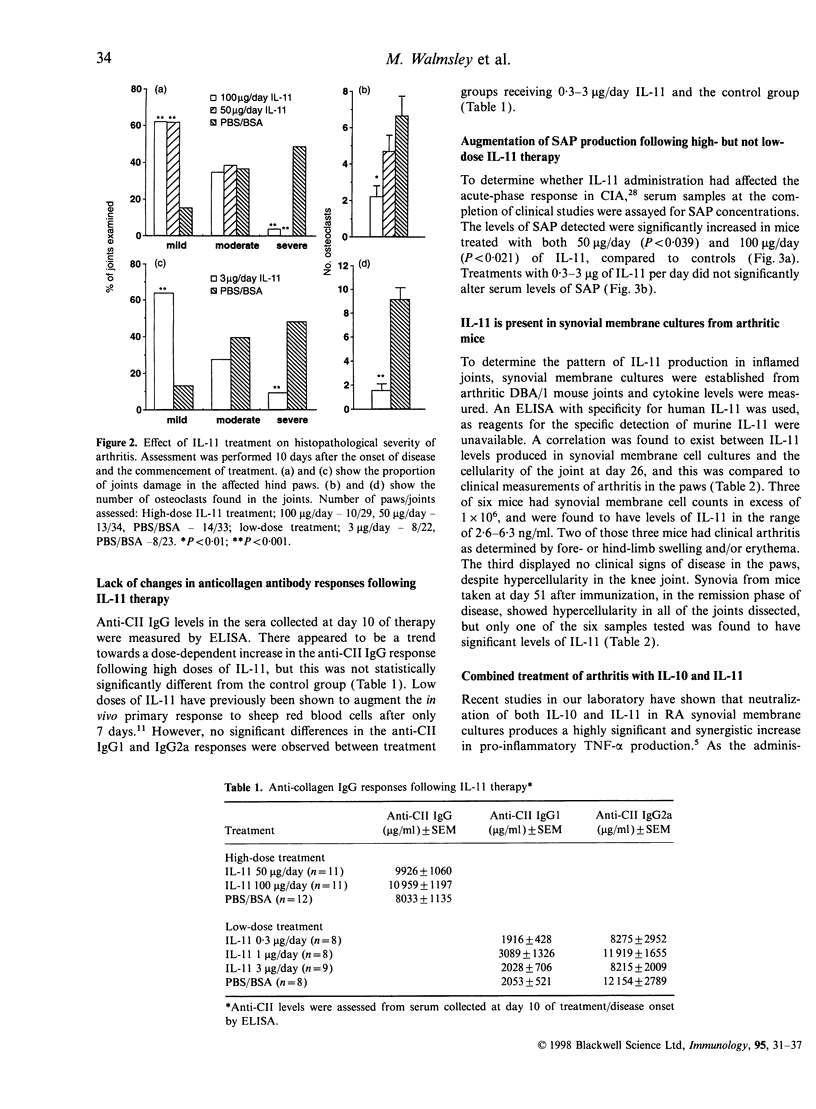
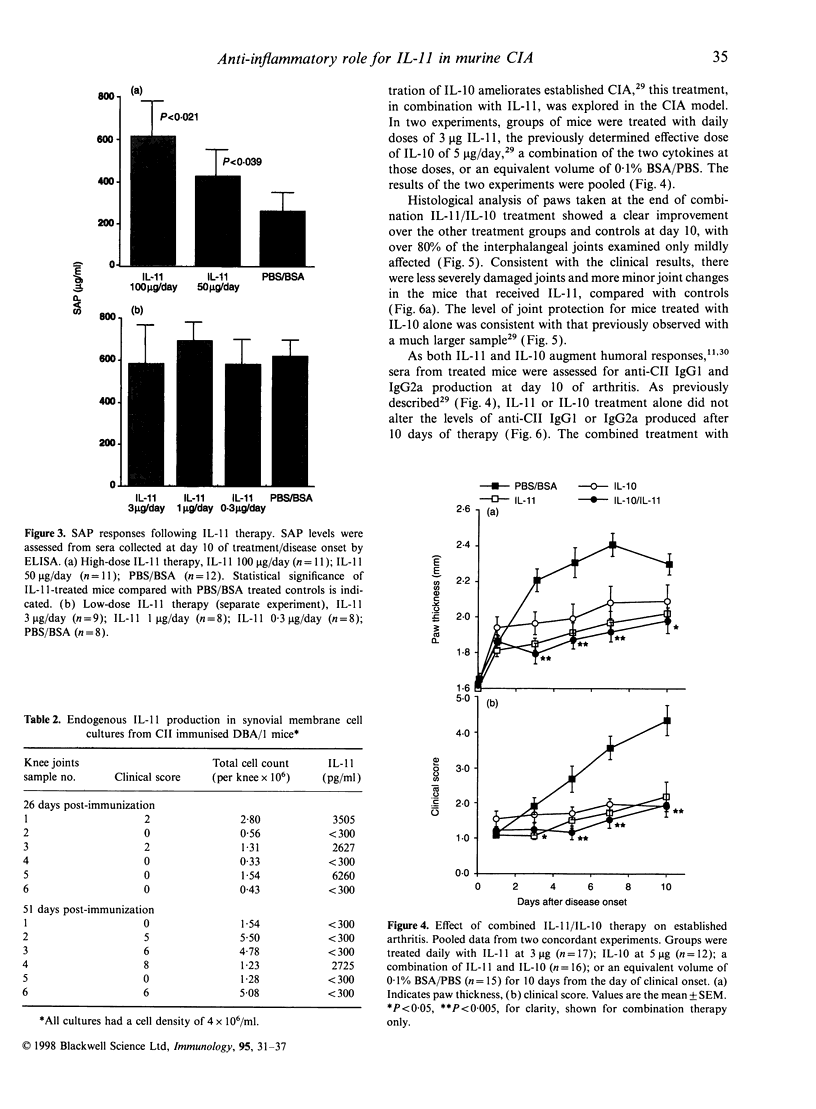
Interleukin-11 (IL-11) is a cytokine belonging to the IL-6 family which has both pro- and anti-inflammatory potential. Like IL-6 it can diminish tumour necrosis factor-alpha and IL-1 production, and augment immunoglobulin synthesis. We have explored the immunomodulatory effects of IL-11 treatment in mice in a model of inflammatory autoimmune joint disease, collagen-induced arthritis (CIA). Recombinant human IL-11 was administered at various doses to DBA/1 mice after the onset of CIA. IL-11 treatment caused a significant reduction in the clinical severity of established CIA, which was associated with protection from joint damage, as assessed by histology. Although there was a suggestion at high doses of IL-11 that the anticollagen type II (CII) response may have been augmented, there was no statistically significant effect of IL-11 treatment on anti-CII antibody levels. Similarly, the acute-phase reactant serum amyloid P was only elevated in mice receiving very high doses (50-100 microgram/day) of IL-11. Endogenous IL-11 was abundantly produced in synovial membrane cultures derived from CII-immunized mice with active disease, suggesting that, as in rheumatoid arthritis, this cytokine is spontaneously produced in the inflammatory response in CIA. The results presented here demonstrate an anti-arthritic immunoregulatory role for IL-11 in murine CIA, and suggest that IL-11 is a candidate therapeutic molecule for human inflammatory arthritic diseases.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson K. C., Morimoto C., Paul S. R., Chauhan D., Williams D., Cochran M., Barut B. A. Interleukin-11 promotes accessory cell-dependent B-cell differentiation in humans. Blood. 1992 Dec 1;80(11):2797–2804. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bliven M. L., Wooley P. H., Pepys M. B., Otterness I. G. Murine type II collagen arthritis. Association of an acute-phase response with clinical course. Arthritis Rheum. 1986 Sep;29(9):1131–1138. doi: 10.1002/art.1780290911. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butler D. M., Malfait A. M., Mason L. J., Warden P. J., Kollias G., Maini R. N., Feldmann M., Brennan F. M. DBA/1 mice expressing the human TNF-alpha transgene develop a severe, erosive arthritis: characterization of the cytokine cascade and cellular composition. J Immunol. 1997 Sep 15;159(6):2867–2876. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Du X. X., Williams D. A. Interleukin-11: a multifunctional growth factor derived from the hematopoietic microenvironment. Blood. 1994 Apr 15;83(8):2023–2030. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elias J. A., Tang W., Horowitz M. C. Cytokine and hormonal stimulation of human osteosarcoma interleukin-11 production. Endocrinology. 1995 Feb;136(2):489–498. doi: 10.1210/endo.136.2.7835281. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Girasole G., Passeri G., Jilka R. L., Manolagas S. C. Interleukin-11: a new cytokine critical for osteoclast development. J Clin Invest. 1994 Apr;93(4):1516–1524. doi: 10.1172/JCI117130. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holmdahl R., Tarkowski A., Jonsson R. Involvement of macrophages and dendritic cells in synovial inflammation of collagen induced arthritis in DBA/1 mice and spontaneous arthritis in MRL/lpr mice. Autoimmunity. 1991;8(4):271–280. doi: 10.3109/08916939109007634. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Horsfall A. C., Butler D. M., Marinova L., Warden P. J., Williams R. O., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Suppression of collagen-induced arthritis by continuous administration of IL-4. J Immunol. 1997 Dec 1;159(11):5687–5696. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katsikis P. D., Chu C. Q., Brennan F. M., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Immunoregulatory role of interleukin 10 in rheumatoid arthritis. J Exp Med. 1994 May 1;179(5):1517–1527. doi: 10.1084/jem.179.5.1517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Keith J. C., Jr, Albert L., Sonis S. T., Pfeiffer C. J., Schaub R. G. IL-11, a pleiotropic cytokine: exciting new effects of IL-11 on gastrointestinal mucosal biology. Stem Cells. 1994;12 (Suppl 1):79–90. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto T., Akira S., Narazaki M., Taga T. Interleukin-6 family of cytokines and gp130. Blood. 1995 Aug 15;86(4):1243–1254. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier R., Ganu V., Lotz M. Interleukin-11, an inducible cytokine in human articular chondrocytes and synoviocytes, stimulates the production of the tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases. J Biol Chem. 1993 Oct 15;268(29):21527–21532. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malfait A. M., Butler D. M., Presky D. H., Maini R. N., Brennan F. M., Feldmann M. Blockade of IL-12 during the induction of collagen-induced arthritis (CIA) markedly attenuates the severity of the arthritis. Clin Exp Immunol. 1998 Feb;111(2):377–383. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-2249.1998.00485.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris J. C., Neben S., Bennett F., Finnerty H., Long A., Beier D. R., Kovacic S., McCoy J. M., DiBlasio-Smith E., La Vallie E. R. Molecular cloning and characterization of murine interleukin-11. Exp Hematol. 1996 Oct;24(12):1369–1376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. R., Barut B. A., Bennett F., Cochran M. A., Anderson K. C. Lack of a role of interleukin 11 in the growth of multiple myeloma. Leuk Res. 1992;16(3):247–252. doi: 10.1016/0145-2126(92)90062-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paul S. R., Bennett F., Calvetti J. A., Kelleher K., Wood C. R., O'Hara R. M., Jr, Leary A. C., Sibley B., Clark S. C., Williams D. A. Molecular cloning of a cDNA encoding interleukin 11, a stromal cell-derived lymphopoietic and hematopoietic cytokine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Oct;87(19):7512–7516. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.19.7512. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romas E., Udagawa N., Zhou H., Tamura T., Saito M., Taga T., Hilton D. J., Suda T., Ng K. W., Martin T. J. The role of gp130-mediated signals in osteoclast development: regulation of interleukin 11 production by osteoblasts and distribution of its receptor in bone marrow cultures. J Exp Med. 1996 Jun 1;183(6):2581–2591. doi: 10.1084/jem.183.6.2581. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rousset F., Garcia E., Defrance T., Péronne C., Vezzio N., Hsu D. H., Kastelein R., Moore K. W., Banchereau J. Interleukin 10 is a potent growth and differentiation factor for activated human B lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Mar 1;89(5):1890–1893. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.5.1890. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Serban D., Rordorf-Adam C. Quantitation of serum amyloid P component by an enzyme-linked immunoassay. J Immunol Methods. 1986 Jun 24;90(2):159–164. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(86)90071-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staines N. A., Wooley P. H. Collagen arthritis--what can it teach us? Br J Rheumatol. 1994 Sep;33(9):798–807. doi: 10.1093/rheumatology/33.9.798. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorbecke G. J., Shah R., Leu C. H., Kuruvilla A. P., Hardison A. M., Palladino M. A. Involvement of endogenous tumor necrosis factor alpha and transforming growth factor beta during induction of collagen type II arthritis in mice. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Aug 15;89(16):7375–7379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.16.7375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trepicchio W. L., Bozza M., Pedneault G., Dorner A. J. Recombinant human IL-11 attenuates the inflammatory response through down-regulation of proinflammatory cytokine release and nitric oxide production. J Immunol. 1996 Oct 15;157(8):3627–3634. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walmsley M., Katsikis P. D., Abney E., Parry S., Williams R. O., Maini R. N., Feldmann M. Interleukin-10 inhibition of the progression of established collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum. 1996 Mar;39(3):495–503. doi: 10.1002/art.1780390318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Feldmann M., Maini R. N. Anti-tumor necrosis factor ameliorates joint disease in murine collagen-induced arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1992 Oct 15;89(20):9784–9788. doi: 10.1073/pnas.89.20.9784. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams R. O., Williams D. G., Maini R. N. Anti-type II collagen ELISA. Increased disease specificity following removal of anionic contaminants from salt-fractionated type II collagen. J Immunol Methods. 1992 Feb 14;147(1):93–100. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wooley P. H., Whalen J. D., Chapman D. L., Berger A. E., Richard K. A., Aspar D. G., Staite N. D. The effect of an interleukin-1 receptor antagonist protein on type II collagen-induced arthritis and antigen-induced arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum. 1993 Sep;36(9):1305–1314. doi: 10.1002/art.1780360915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yin T. G., Schendel P., Yang Y. C. Enhancement of in vitro and in vivo antigen-specific antibody responses by interleukin 11. J Exp Med. 1992 Jan 1;175(1):211–216. doi: 10.1084/jem.175.1.211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van den Berg W. B., Joosten L. A., Helsen M., van de Loo F. A. Amelioration of established murine collagen-induced arthritis with anti-IL-1 treatment. Clin Exp Immunol. 1994 Feb;95(2):237–243. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2249.1994.tb06517.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]