Fig. 6.
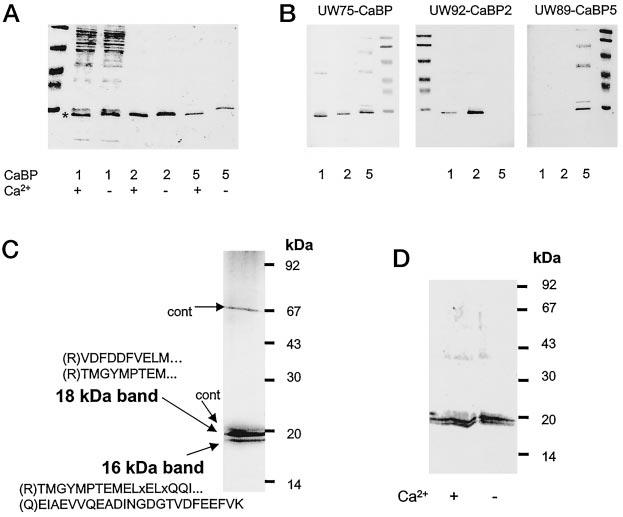
Specificities of anti-CaBP antibodies and purification of retinal CaBPs. A, Ca2+-dependent mobility change in SDS-PAGE for partially purified CaBP1 (purified on DEAE-cellulose; see “Materials and Methods”), CaBP2-His6 purified on Ni2+-chelex column, CaBP5-His6 purified on Ni2+-chelex column. B, immunoreactivity of CaBP1, CaBP2, and CaBP5 with UW75 (raised against the common domain of CaBP), UW92 (raised against CaBP2), and UW89 (raised against CaBP5). C, retinal CaBPs were purified as described under “Materials and Methods” and blotted on polyvinylidene difluoride. The protein bands were digested with trypsin, and peptides were separated on a reverse phase column. The aa sequence of peptides was obtained using a combination of Edman degradation of matrix-assisted laser desorption/ionization (MALDI; see “Materials and Methods”). In brackets are the predicted residues from the cDNA sequence and the N-terminal side of tryptic digestion: x represent an undetermined aa, dotted points show that the sequence did not reach the end of the peptide. cont, contaminants from UW72. D, Western blot of retinal CaBPs probed with UW72 in the presence or absence of 100 μm [Ca2+].
