Figure 1. Aβ induced a decrease in dynamin levels in a dose- and time-dependent manner in cultured hippocampal neurons.
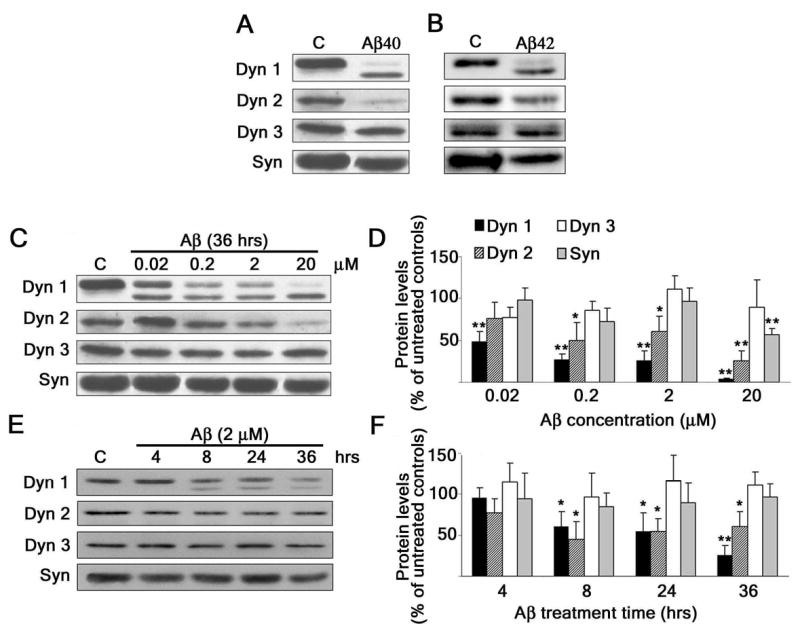
(A and B) Western blot analysis of dynamin 1 (Dyn 1), dynamin 2 (Dyn 2), dynamin 3 (Dyn 3), and synaptophysin (Syn) content in whole cell extracts prepared from 21-DIV hippocampal neurons cultured in the absence (c) or in the presence of Aβ1–40 or Aβ 1–42 (20 μM) for 36 hours. Note the decrease in Dyn 1 (100-kDa) and Dyn 2 immunoreactive bands and the appearance of a second Dyn 1 (~90-kDa) immunoreactive band in Aβ-treated neurons. (C and E) Western blot analysis of dynamin and synaptophysin content in whole cell extracts prepared from 21-DIV hippocampal neurons cultured with increasing concentrations of Aβ for 36 hours (C) or cultured in the presence of Aβ 2 (μM) for up to 36 hrs (E). (D and F) Quantification analysis of the dose-response (C) and time-course (E) effects of Aβ in cultured hippocampal neurons. The results were normalized using tubulin as internal controls. The values obtained in untreated controls were considered 100%. Values represent the mean ± SEM obtained from 6–8 independent experiments. Differs from untreated controls, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
