Figure 4. Aβ induced the reduction of dynamin 1 both at transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels in cultured hippocampal neurons.
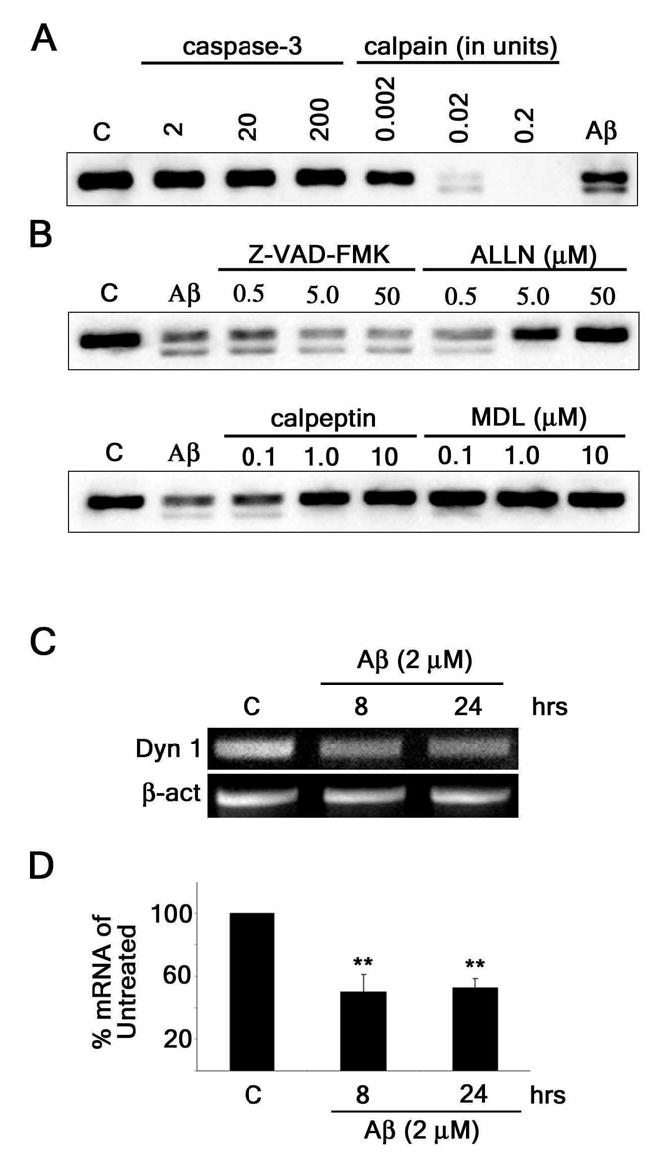
(A) Western blot analysis of dynamin 1 (Dyn 1) content in whole cell extracts obtained from 21-DIV hippocampal neurons incubated in the presence of increasing concentrations of recombinant caspase-3 or calpain. Note that calpain incubation produced a lower molecular weight dynamin 1 immunoreactive band (~90-kDa) similar to the one obtained when cultured hippocampal neurons were treated with Aβ (Aβ). (B) Western blot analysis of dynamin 1 content in whole cell extracts prepared from 21-DIV hippocampal neurons treated with increasing concentrations of various protease inhibitors for 1 hour prior to the addition of Aβ (2μM). Inhibitors included a general caspase inhibitor (VAD), a calpain/proteosome inhibitor (ALLN), and calpain inhibitors (calpeptin and MDL). Only inhibitors blocking calpain activity prevented cleavage of dynamin 1. (C) Conventional RT-PCR analysis of dynamin 1 mRNA bands in untreated and Aβ-treated (2 μM) cultured hippocampal neurons. β-actin was used as an internal control. (D) Real-time RT-PCR of dynamin 1 mRNA in untreated and Aβ-treated (2μM) cultured hippocampal neurons. Dynamin 1 signal was normalized using the 18s ribosomal gene as an endogenous control. Values obtained in untreated controls were set at 100%. Values represent the mean ± SEM obtained from 6 independent experiments. Differs from untreated controls, *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01
