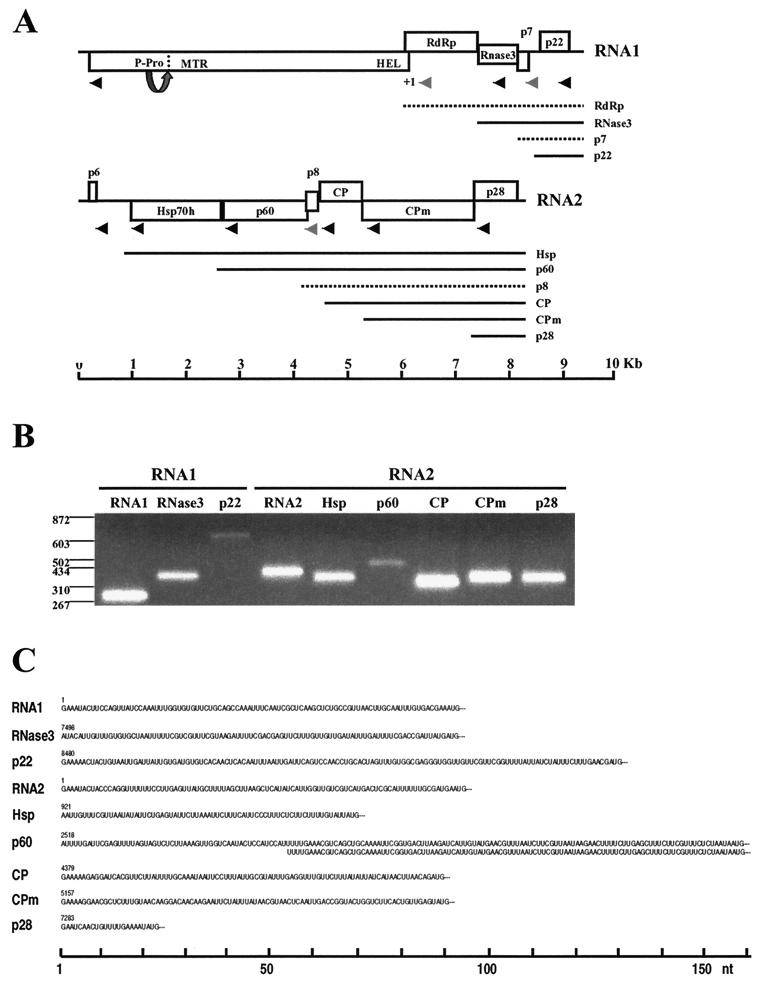
FIG. 1.
Genomic structure of SPCSV and expression of sgRNAs. (A) The genomic RNA1 and RNA2 are represented by a line, with the ORFs indicated by boxes. ORFs are shown above, below, or in the middle of the line, indicating that they are found in different reading frames. On RNA1, +1 indicates a putative +1 ribosomal frameshift site. The functional domains predicted from the deduced amino acid sequence are indicated inside the boxes, or, if no function could be predicted, the approximate molecular weight is indicated. P-Pro, putative papain-like leader proteinase, for which the arrow and dotted line indicate the predicted autocatalytic cleavage site; MTR, methyltransferase domain; HEL, helicase domain; RdRp, RNA-dependant RNA polymerase domain; RNase3, RNase III-like domain; Hsp70h, heat shock protein 70 family homologue; CP, coat protein; CPm, minor coat protein. The lines below the genomic RNA indicate sgRNAs, each of which was named according to the first ORF at the 5′ end. Dashed lines indicate hypothetical sgRNAs that were not detected with the GeneRacer method. Arrowheads indicate the positions of primers used for amplification of the 5′ ends from the genomic and sgRNAs with GeneRacer, the products of which are shown in panel B (2% agarose gel; positions of molecular size markers [in nucleotides] are shown to the left). Grey arrowheads in panel A indicate that no product was obtained in GeneRacer with these primers. (C) The 5′ untranslated sequences of the sgRNAs are shown, as determined from PCR products obtained with GeneRacer. Amplification of the p60 sgRNA 5′ end resulted in two fragments, of which one was 53 nt shorter but otherwise identical.