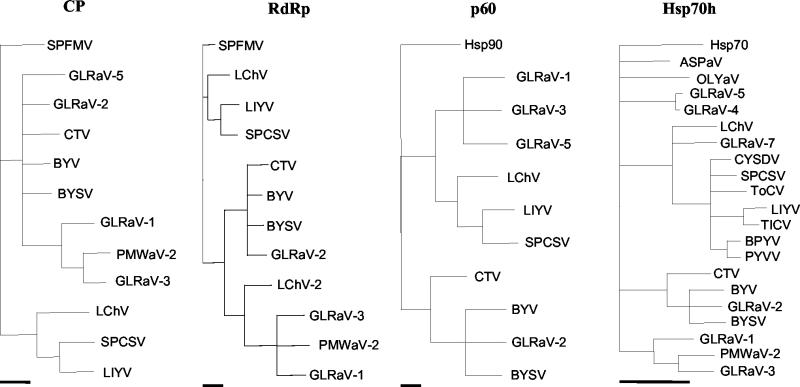
FIG. 5.
Phylogenetic analysis of the amino acid sequences deduced for the coat protein (CP), RNA-dependent RNA polymerase (RdRp), p60, and the N-proximal ATPase domain of the Hsp70h of clostero- and criniviruses. Alignments were made with the Clustal algorithm (27), and the trees were generated with the maximum parsimony algorithm (16, 22). Clades supported by less than 70% of the bootstrap replicates were collapsed. In the analysis of the CP and RdRp sequences, the sequence of the corresponding protein of Sweet potato feathery mottle virus (genus Potyvirus, family Potyviridae; BAA07546) was used as an outgroup, whereas in the analysis of the p60 and Hsp70h sequences, the Hsp90 of Arabidopsis thaliana (NP_194150) and Hsp70 of tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum; P34935) were used as outgroups, respectively. The bars below each tree indicate a distance of 10 parsimonious steps. See Table 1 for virus acronyms and references.