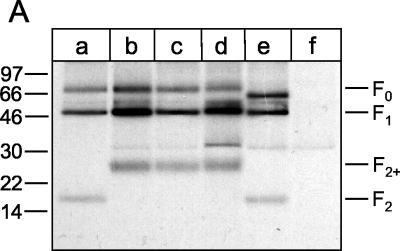
FIG. 2.
Proteolytic processing of parental and mutant F proteins of recombinant BRSVs. (A) PT-11 cells were infected with recombinant BRSVs at an MOI of 0.1. At 40 h after infection, the cells were metabolically labeled with [35S]methionine-[35S]cysteine for 1 h, and F protein was immunoprecipitated from the cell lysates. The immunoprecipitates were separated by Tricine-SDS-10% polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis under reducing conditions and detected by autoradiography [lane a, rBRSV-F(parental); lane b, rBRSV-F(R106N/K108N); lane c, rBRSV-F(K108N/R109N); lane d, rBRSV-F(R106S/K108N/R109N); lane e, rBRSV-F(Δ106-130); lane f, noninfected cells]. (B) PT-11 cells were infected with recombinant BRSVs at an MOI of 0.1 and maintained in medium either in the absence or presence of trypsin (as indicated at the top of the gel). After 4 days, the viruses were harvested from the cell culture supernatant and then pelleted by ultracentrifugation. The viruses were solubilized by SDS sample buffer and run on an SDS-8% polyacrylamide gel under nonreducing conditions [lanes a and b, rBRSV-F(parental); lanes c and d, rBRSV-F(R106N/K108N); lanes e and f, rBRSV-F(K108N/R109N); lanes g and h, rBRSV-F(R106S/K108N/R109N); lanes i and j, rBRSV-F(Δ106-130)]. F protein was detected by conventional Western blot technique with a mixture of three monoclonal antibodies directed to this protein. The relative positions of standard proteins (with the molecular masses indicated in kilodaltons) are shown on the left.