Abstract
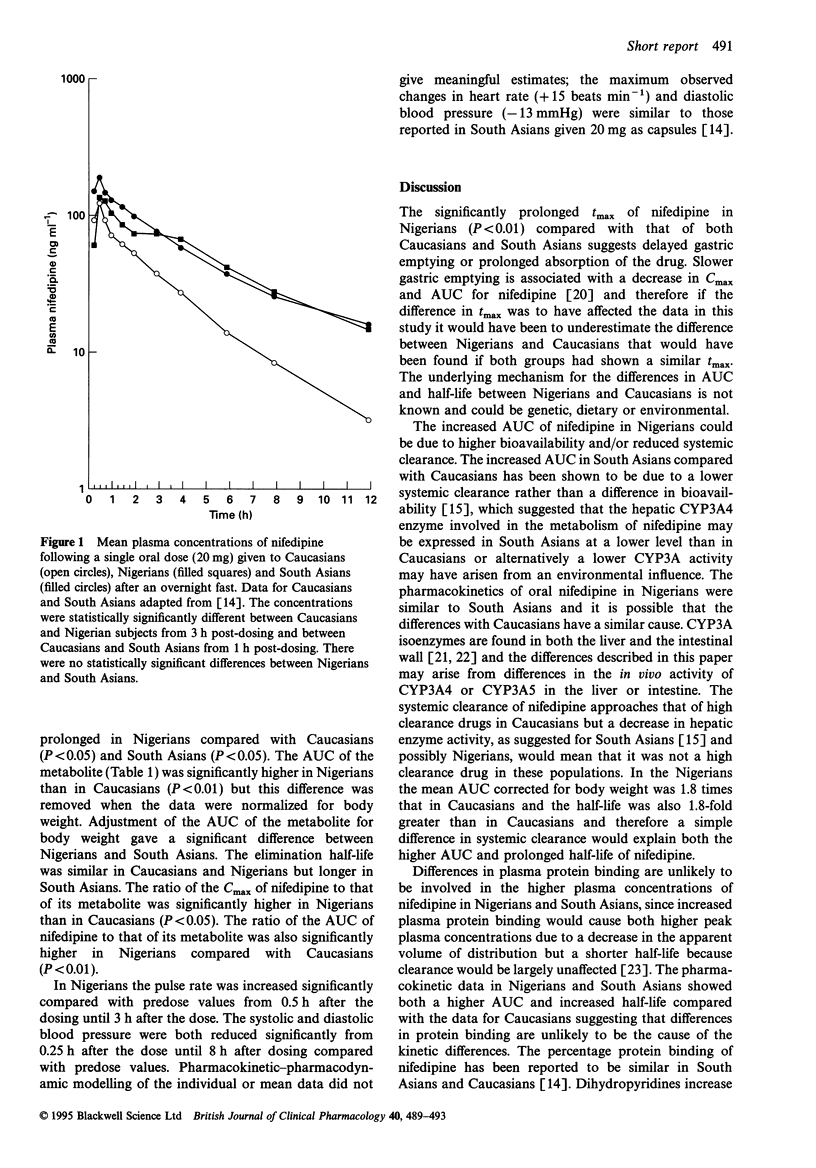
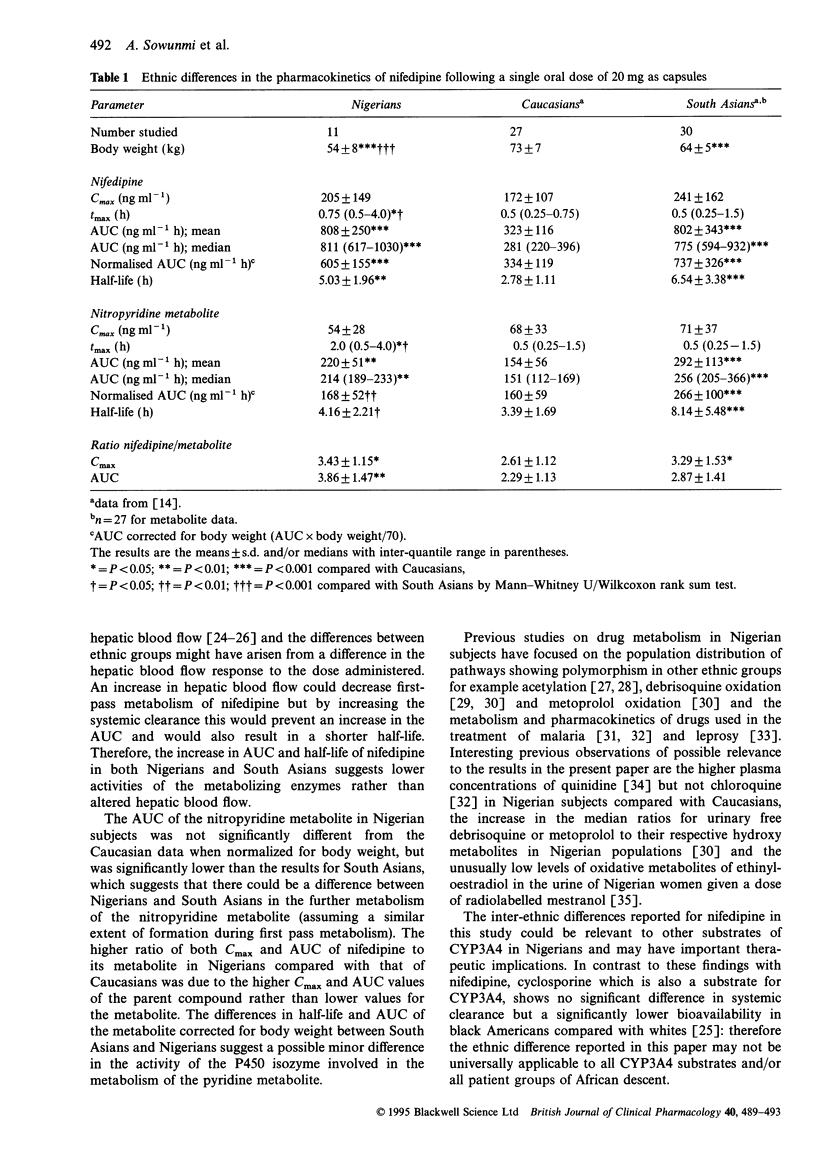
Nifedipine was administered to 12 healthy Nigerian volunteers as a single oral dose of 20 mg capsule under fasting conditions. The pharmacokinetic results were compared with published data using the same protocol and analytical method for 27 Caucasians and 30 South Asians. The area under the plasma concentration-time curve (AUC) of nifedipine in Nigerians (808 +/- 250 ng ml-1 h) was significantly higher (P < 0.001) than that in Caucasians (323 +/- 116 ng ml-1 h) and the difference remained significant (P < 0.001) when corrected for body weight. The elimination half-life was also significantly higher (P < 0.01) in Nigerians (5.03 +/- 1.96 h) than in Caucasians (2.78 +/- 1.11 h). No significant differences were observed between Nigerians and South Asians in either AUC or half-life of nifedipine. The AUC of the nitropyridine metabolite was higher (P < 0.01) in Nigerians (220 +/- 51 ng ml-1 h) compared with that in Caucasians (154 +/- 56 ng ml-1 h) but the difference was not maintained when corrected for body weight. The AUC corrected for body weight and the elimination half-life of the metabolite were significantly higher in South Asians compared with those of Nigerians and Caucasians. The pharmacokinetics of oral nifedipine in Nigerians were similar to those in South Asians and therefore may also arise from a lower systemic clearance compared with Caucasians as has been reported previously for South Asians.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahsan C. H., Renwick A. G., Waller D. G., Challenor V. F., George C. F., Amanullah M. The influence of dose and ethnic origins on the pharmacokinetics of nifedipine. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1993 Sep;54(3):329–338. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1993.155. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauer L. A., Murray K., Horn J. R., Opheim K., Olsen J. Influence of nifedipine therapy on indocyanine green and oral propranolol pharmacokinetics. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1989;37(3):257–260. doi: 10.1007/BF00679780. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Challenor V. F., Waller D. G., Renwick A. G., Gruchy B. S., George C. F. The trans-hepatic extraction of nifedipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Oct;24(4):473–477. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03200.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark D. W. Genetically determined variability in acetylation and oxidation. Therapeutic implications. Drugs. 1985 Apr;29(4):342–375. doi: 10.2165/00003495-198529040-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Essien E. E., Ifudu N. D. Residual chloroquine and metabolites in man as a sequel of previous chloroquine medications: a urinary excretion study and its significance. J Trop Med Hyg. 1984 Jun;87(3):131–136. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans W. E., Relling M. V., Rahman A., McLeod H. L., Scott E. P., Lin J. S. Genetic basis for a lower prevalence of deficient CYP2D6 oxidative drug metabolism phenotypes in black Americans. J Clin Invest. 1993 May;91(5):2150–2154. doi: 10.1172/JCI116441. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feely J. Nifedipine increases and glyceryl trinitrate decreases apparent liver blood flow in normal subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Jan;17(1):83–85. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb05003.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J. The molecular biology of cytochrome P450s. Pharmacol Rev. 1988 Dec;40(4):243–288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guengerich F. P. Oxidative cleavage of carboxylic esters by cytochrome P-450. J Biol Chem. 1987 Jun 25;262(18):8459–8462. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoyo-Vadillo C., Castañeda-Hernández G., Herrera J. E., Vidal-Gárate J., Moreno-Ramos A., Chávez F., Hong E. Pharmacokinetics of nifedipine slow release tablet in Mexican subjects: further evidence for an oxidation polymorphism. J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Sep;29(9):816–820. doi: 10.1002/j.1552-4604.1989.tb03425.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyun A. O., Lennard M. S., Tucker G. T., Woods H. F. Metoprolol and debrisoquin metabolism in Nigerians: lack of evidence for polymorphic oxidation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Oct;40(4):387–394. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iyun A. O., Lennard M. S., Tucker G. T., Woods H. F. Metoprolol and debrisoquin metabolism in Nigerians: lack of evidence for polymorphic oxidation. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1986 Oct;40(4):387–394. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1986.195. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeyakumar L. H., French M. R. Acetylator phenotype among individuals with glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase variants. Xenobiotica. 1986 Dec;16(12):1129–1132. doi: 10.3109/00498258609038990. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeyakumar L. H., French M. R. Polymorphic acetylation of sulfamethazine in a Nigerian (Yoruba) population. Xenobiotica. 1981 May;11(5):319–321. doi: 10.3109/00498258109045310. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kolars J. C., Lown K. S., Schmiedlin-Ren P., Ghosh M., Fang C., Wrighton S. A., Merion R. M., Watkins P. B. CYP3A gene expression in human gut epithelium. Pharmacogenetics. 1994 Oct;4(5):247–259. doi: 10.1097/00008571-199410000-00003. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindholm A., Welsh M., Alton C., Kahan B. D. Demographic factors influencing cyclosporine pharmacokinetic parameters in patients with uremia: racial differences in bioavailability. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Oct;52(4):359–371. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.156. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lou Y. C. Differences in drug metabolism polymorphism between Orientals and Caucasians. Drug Metab Rev. 1990;22(5):451–475. doi: 10.3109/03602539008991447. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lown K. S., Kolars J. C., Thummel K. E., Barnett J. L., Kunze K. L., Wrighton S. A., Watkins P. B. Interpatient heterogeneity in expression of CYP3A4 and CYP3A5 in small bowel. Lack of prediction by the erythromycin breath test. Drug Metab Dispos. 1994 Nov-Dec;22(6):947–955. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- M'Buyamba-Kabangu J. R., Tambwe M. The efficacy of beta-adrenoceptor and calcium-entry blockers in hypertensive blacks. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 1990 Mar;4 (Suppl 2):389–394. doi: 10.1007/BF02603182. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mbanefo C., Bababunmi E. A., Mahgoub A., Sloan T. P., Idle J. R., Smith R. L. A study of the debrisoquine hydroxylation polymorphism in a Nigerian population. Xenobiotica. 1980 Nov;10(11):811–818. doi: 10.3109/00498258009033811. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olatunde A., Price Evans D. A. Blood quinidine levels and cardiac effects in white British and Nigerian subjects. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1982 Oct;14(4):513–518. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1982.tb02022.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pieters F. A., Woonink F., Zuidema J. Influence of once-monthly rifampicin and daily clofazimine on the pharmacokinetics of dapsone in leprosy patients in Nigeria. Eur J Clin Pharmacol. 1988;34(1):73–76. doi: 10.1007/BF01061421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulter N. R., Sanderson J. E., Thompson A. V., Sever P. S., Chang C. L. Comparison of nifedipine and propranolol as second line agent for hypertension in black Kenyans. BMJ. 1993 Mar 6;306(6878):621–622. doi: 10.1136/bmj.306.6878.621. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rashid T. J., Martin U., Clarke H., Waller D. G., Renwick A. G., George C. F. Factors affecting the absolute bioavailability of nifedipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1995 Jul;40(1):51–58. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1995.tb04534.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relling M. V., Cherrie J., Schell M. J., Petros W. P., Meyer W. H., Evans W. E. Lower prevalence of the debrisoquin oxidative poor metabolizer phenotype in American black versus white subjects. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1991 Sep;50(3):308–313. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1991.141. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Relling M. V., Lin J. S., Ayers G. D., Evans W. E. Racial and gender differences in N-acetyltransferase, xanthine oxidase, and CYP1A2 activities. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1992 Dec;52(6):643–658. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1992.203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Renwick A. G., Ahsan C. H., Challenor V. F., Daniels R., Macklin B. S., Waller D. G., George C. F. The influence of posture on the pharmacokinetics of orally administered nifedipine. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1992 Oct;34(4):332–336. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1992.tb05639.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Routledge P. A. The plasma protein binding of basic drugs. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1986 Nov;22(5):499–506. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1986.tb02927.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker O., Salako L. A., Alván G., Ericsson O., Sjöqvist F. The disposition of chloroquine in healthy Nigerians after single intravenous and oral doses. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1987 Mar;23(3):295–301. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1987.tb03048.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waller D. G., Renwick A. G., Gruchy B. S., George C. F. The first pass metabolism of nifedipine in man. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1984 Dec;18(6):951–954. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1984.tb02569.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watkins P. B., Wrighton S. A., Schuetz E. G., Molowa D. T., Guzelian P. S. Identification of glucocorticoid-inducible cytochromes P-450 in the intestinal mucosa of rats and man. J Clin Invest. 1987 Oct;80(4):1029–1036. doi: 10.1172/JCI113156. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams M. C., Goldzieher J. W. Chromatographic patterns of urinary ethynyl estrogen metabolites in various populations. Steroids. 1980 Sep;36(3):255–282. doi: 10.1016/0039-128x(80)90001-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood A. J., Zhou H. H. Ethnic differences in drug disposition and responsiveness. Clin Pharmacokinet. 1991 May;20(5):350–373. doi: 10.2165/00003088-199120050-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woolhouse N. M., Eichelbaum M., Oates N. S., Idle J. R., Smith R. L. Dissociation of co-regulatory control of debrisoquin/phenformin and sparteine oxidation in Ghanaians. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 1985 May;37(5):512–521. doi: 10.1038/clpt.1985.81. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Harten J., Burggraaf J., Danhof M., van Brummelen P., Breimer D. D. The contribution of nisoldipine-induced changes in liver blood flow to its pharmacokinetics after oral administration. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 May;27(5):581–586. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2125.1989.tb03420.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


