Abstract
1. A method is described for resolving isometric tetanic tension developed by fast-twitch and slow-graded components of heterogeneous toad muscles. This makes use of the difference in threshold for excitation of low threshold nerve fibres which normally innervate the fast-twitch muscle fibres and high threshold nerve fibres which innervate slow-graded muscle fibres.
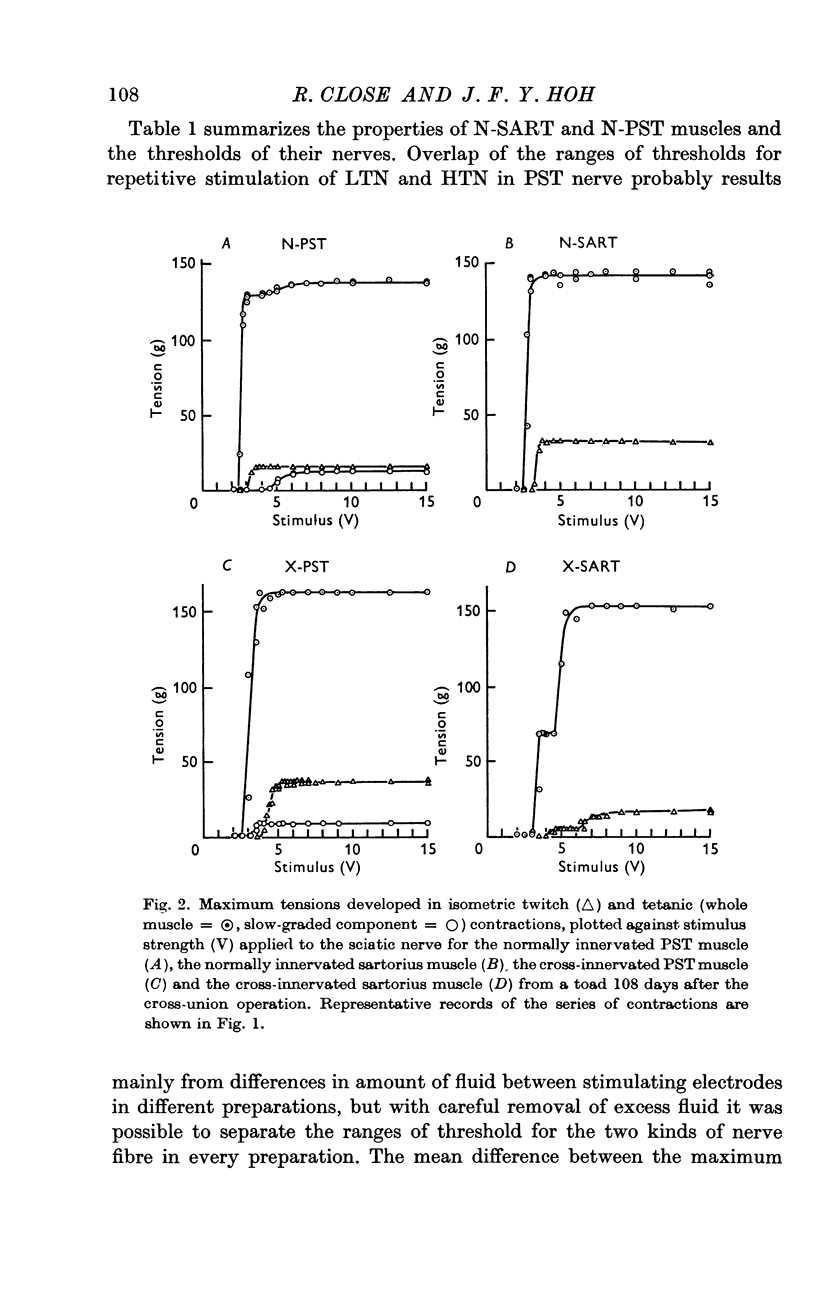
2. The sartorius muscle contains only fast-twitch muscle fibres whereas the posterior semitendinosus (PST) contains both fast-twitch and slow-graded muscle fibres, the latter contributing 10-15% of the maximum isometric tetanic tension.
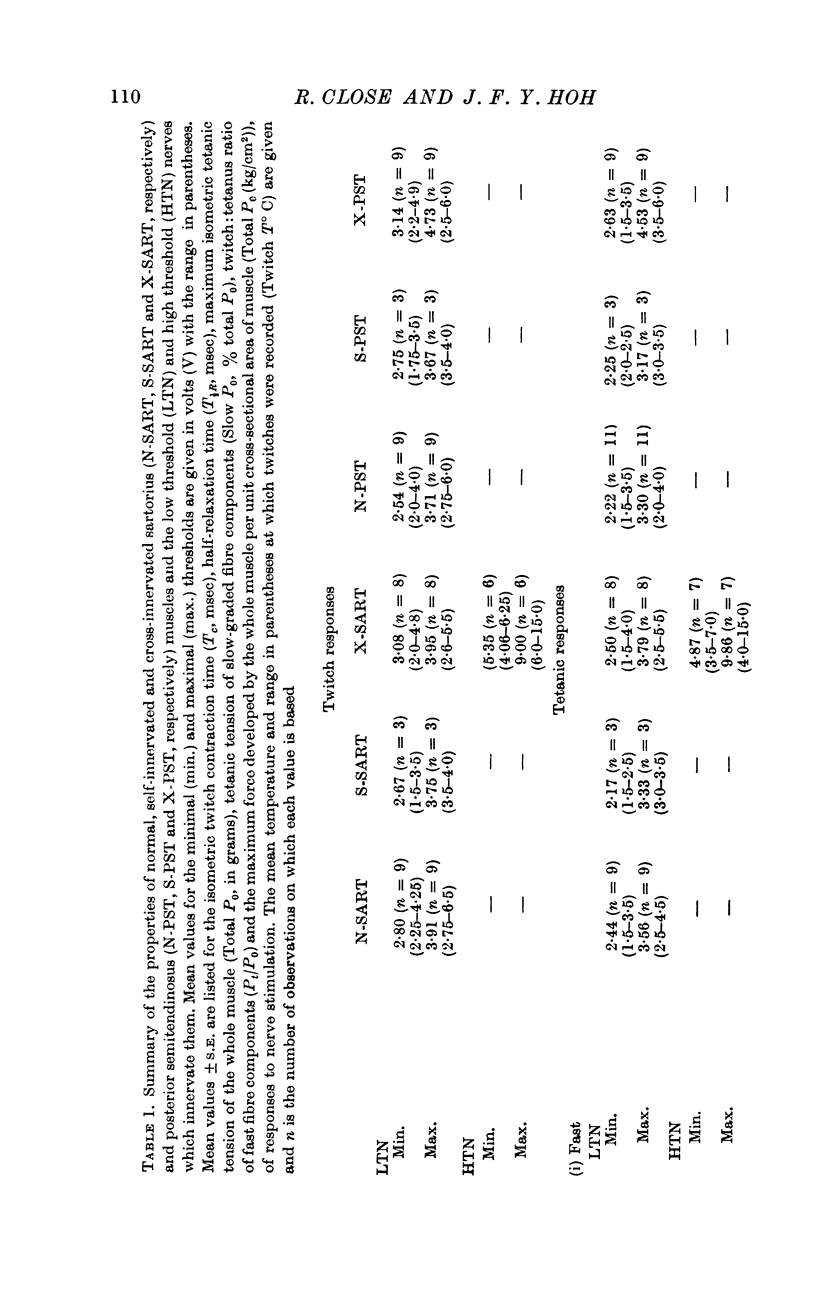
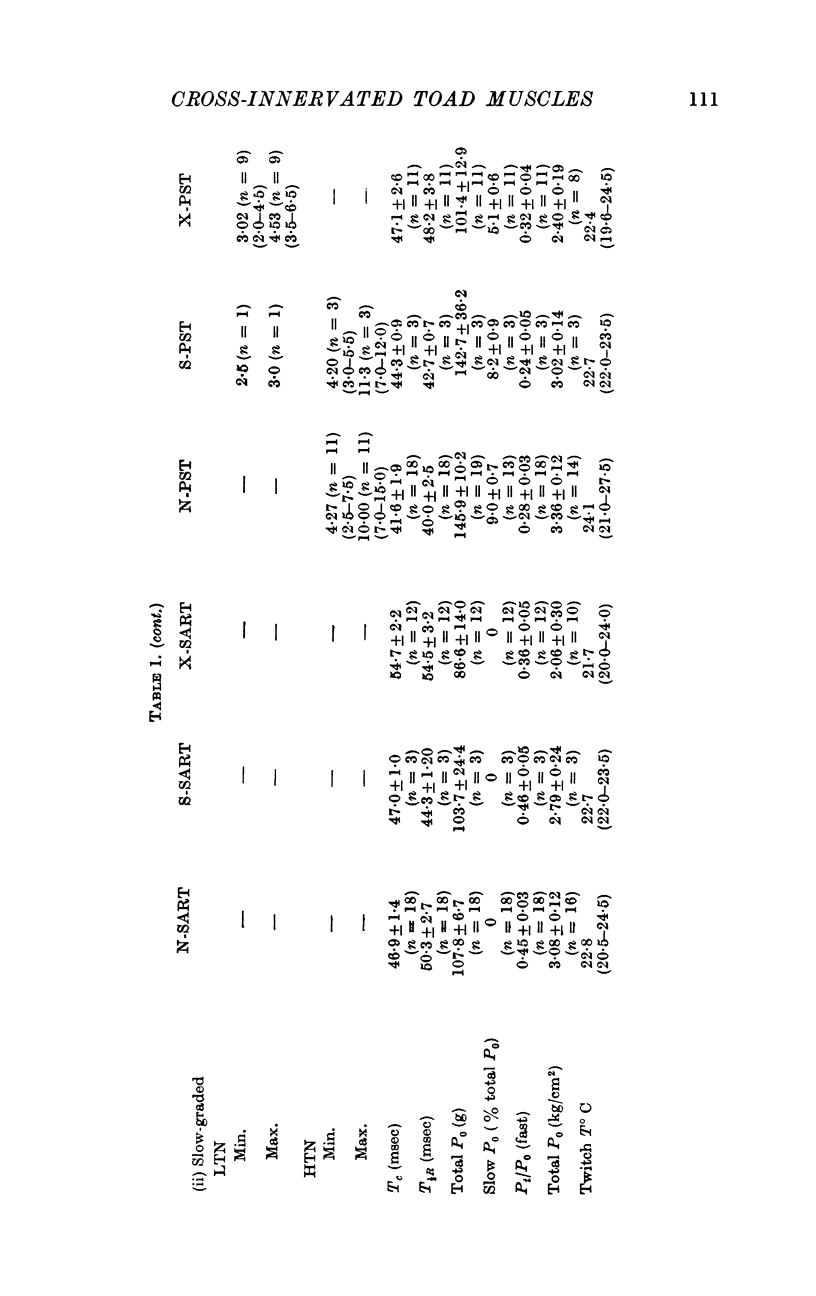
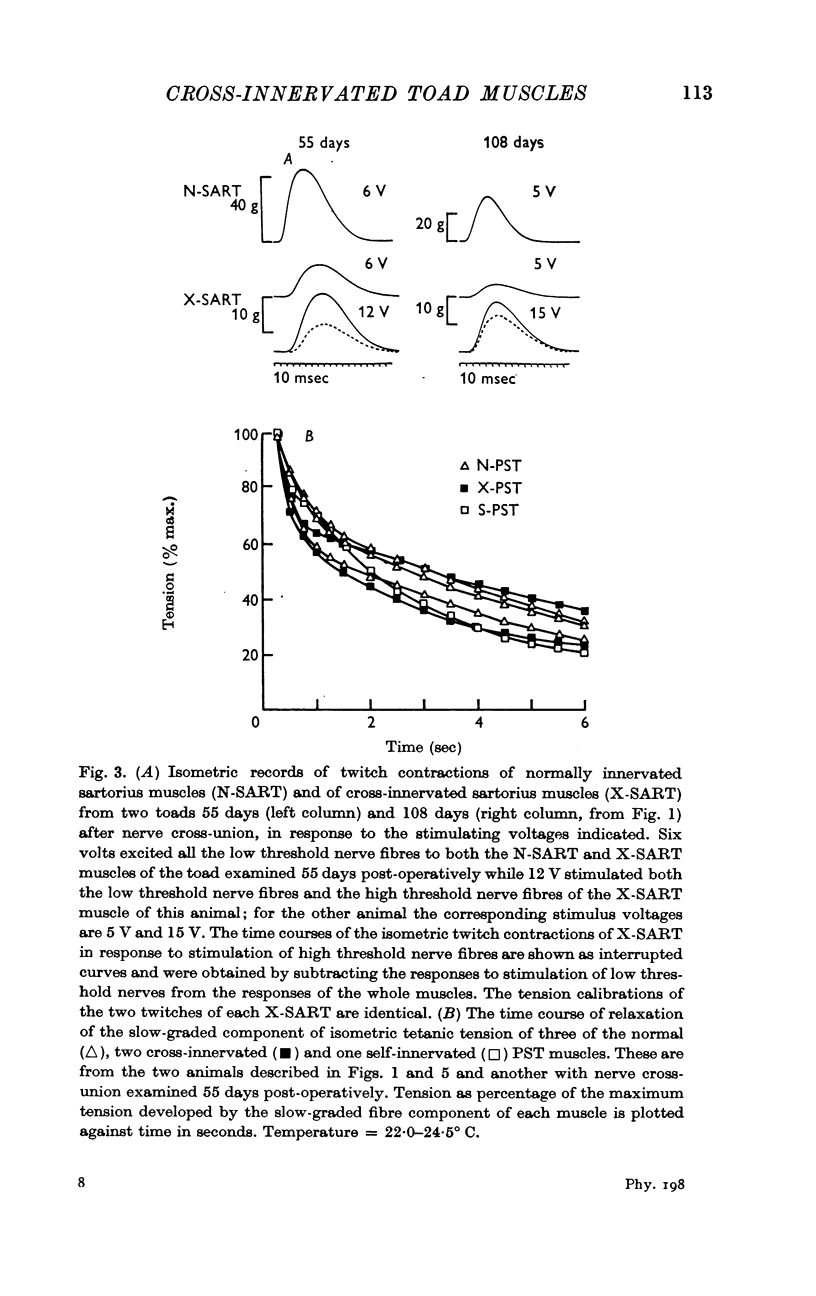
3. Following surgical cross-union of nerve to sartorius and PST muscles, both the fast-twitch and slow-graded muscle fibre components of the PST are reinnervated by low threshold nerves originally innervating sartorius fast-twitch fibres, and sartorius fast-twitch muscle fibres are reinnervated by both low threshold and high threshold nerves formerly supplying the fast-twitch and slow-graded muscle fibre components of the PST.
4. The characteristic mechanical responses of fast-twitch muscle fibres and slow-graded muscle fibres were not transformed up to 134 and 200 days respectively following nerve cross-union.
5. PST nerve partially innervated the sartorius muscle whereas sartorius nerves completely innervated the PST muscle. Isometric tetanic tension declined markedly during repetitive indirect stimulation of cross-innervated sartorius muscles, whereas the tetanic contractions of cross-innervated PST showed a plateau of tension and resembled the response of normal muscles.
6. Normal, cross-innervated and self-innervated PST muscles gave sustained contractures in the presence of acetylcholine whereas PST muscles denervated for 120 days gave phasic contractures similar to those of normal, cross-innervated and self-innervated sartorius muscles.
Full text
PDF















Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aitken J. T., Sharman M., Young J. Z. Maturation of regenerating nerve fibres with various peripheral connexions. J Anat. 1947 Jan;81(Pt 1):1–22.2. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aitken J. T. The effect of peripheral connexions on the maturation of regenerating nerve fibres. J Anat. 1949 Jan;83(Pt 1):32–43. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BERNSTEIN J. J., GUTH L. Nonselectivity in establishment of neuromuscular connections following nerve regeneration in the rat. Exp Neurol. 1961 Sep;4:262–275. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(61)90047-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BOYD I. A. Uniform staining of nerve endings in skeletal muscle with gold chloride. Stain Technol. 1962 Jul;37:225–230. doi: 10.3109/10520296209117741. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., ECCLES J. C., ECCLES R. M. Interactions between motoneurones and muscles in respect of the characteristic speeds of their responses. J Physiol. 1960 Feb;150:417–439. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006395. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BULLER A. J., LEWIS D. M. FURTHER OBSERVATIONS ON MAMMALIAN CROSS-INNERVATED SKELETAL MUSCLE. J Physiol. 1965 May;178:343–358. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1965.sp007631. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Close R. Effects of cross-union of motor nerves to fast and slow skeletal muscles. Nature. 1965 May 22;206(4986):831–832. doi: 10.1038/206831a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dubowitz V. Cross-innervated mammalian skeletal muscle: histochemical, physiological and biochemical observations. J Physiol. 1967 Dec;193(3):481–496.3. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008373. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elsberg C. A. EXPERIMENTS ON MOTOR NERVE REGENERATION AND THE DIRECT NEUROTIZATION OF PARALYZED MUSCLES BY THEIR OWN AND BY FOREIGN NERVES. Science. 1917 Mar 30;45(1161):318–320. doi: 10.1126/science.45.1161.318. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- GRAY E. G. The spindle and extrafusal innervation of a frog muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1957 May 7;146(924):416–430. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1957.0021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HESS A. The structure of extrafusal muscle fibers in the frog and their innervation studied by the cholinesterase technique. Am J Anat. 1960 Sep;107:129–151. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001070204. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hník P., Jirmanová I., Vyklický L., Zelená J. Fast and slow muscles of the chick after nerve cross-union. J Physiol. 1967 Nov;193(2):309–325. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRNJEVIC K., MILEDI R. Failure of neuromuscular propagation in rats. J Physiol. 1958 Mar 11;140(3):440–461. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KUFFLER S. W., VAUGHAN WILLIAMS E. M. Small-nerve junctional potentials; the distribution of small motor nerves to frog skeletal muscle, and the membrane characteristics of the fibres they innervate. J Physiol. 1953 Aug;121(2):289–317. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1953.sp004948. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LAENNERGREN J. FAT IN TWITCH AND SLOW MUSCLE FIBRES. Acta Physiol Scand. 1965 Jan-Feb;63:193–194. doi: 10.1111/j.1748-1716.1965.tb04058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MILEDI R. Properties of regenerating neuromuscular synapses in the frog. J Physiol. 1960 Nov;154:190–205. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1960.sp006573. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miledi R., Orkand P. Effect of a "fast" nerve on "slow" muscle fibres in the frog. Nature. 1966 Feb 12;209(5024):717–718. doi: 10.1038/209717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Romanul F. C., Van der Meulen J. P. Slow and fast muscles after cross innervation. Enzymatic and physiological changes. Arch Neurol. 1967 Oct;17(4):387–402. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1967.00470280053006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sperry R. W., Arora H. L. Selectivity in regeneration of the oculomotor nerve in the cichlid fish, Astronotus ocellatus. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1965 Dec;14(3):307–317. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THOMSON J. D., MORGAN J. A., HINES H. M. Physiologic characteristics of regenerating mammalian nerve and muscle. Am J Physiol. 1950 Apr 1;161(1):142–150. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1950.161.1.142. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomanek R. J., Tipton C. M. Influence of exercise and tenectomy on the morphology of a muscle nerve. Anat Rec. 1967 Sep;159(1):105–113. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091590114. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zelená J., Vyklický L., Jirmanová I. Motor end-plates in fast and slow muscles of the chick after cross-union of their nerves. Nature. 1967 Jun 3;214(5092):1010–1011. doi: 10.1038/2141010a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


