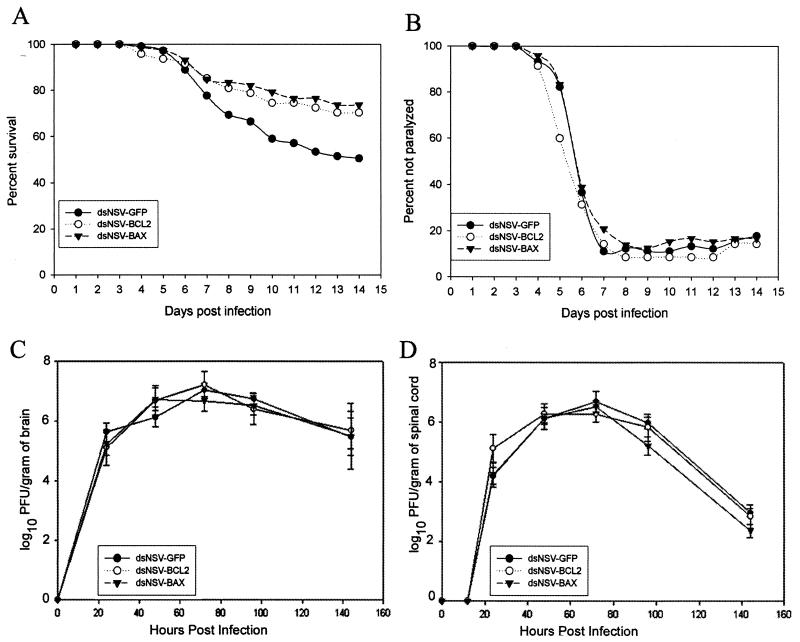
FIG. 3.
Overexpression of BCL-2 family members alters survival but not paralysis caused by dsNSV infection. (A) Percentage of 4-week-old mice (at least 75 per group, in four separate experiments) that survived intracerebral inoculation with 103 PFU of either dsNSV-GFP, dsNSV-BCL-2, or dsNSV-BAX. BCL-2 and BAX are both protective compared to GFP (P < 0.04 and P < 0.004, respectively). (B) Percentage of animals that did not develop hind-limb paralysis following infection. The risk of paralysis among dsNSV-BCL-2-infected mice compared to dsNSV-GFP-infected mice generated an OR of 0.87 (P = 0.19). The risk of paralysis among dsNSV-BAX-infected mice compared to dsNSV-GFP-infected mice generated an OR of 1.09 (P = 0.32). (C and D) Replication of recombinant dsNSV-derived viruses in the brains (C) and spinal cords (D) of infected mice. Each point represents the mean and SEM log10 PFU per gram of tissue from at least three animals. None of the brain or spinal cord viral growth curves was statistically different from one another.