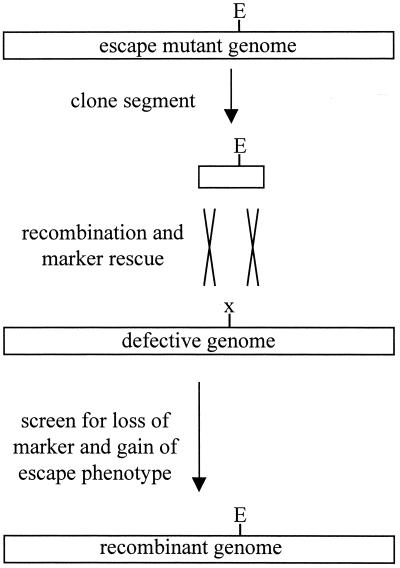
FIG. 1.
Marker rescue strategy. To map escape mutations (E), a region of the mutant phage genome was cloned into a plasmid and introduced into Salmonella. The cells were then infected with a phage that contains a conditional selectable marker (x) under permissive conditions. During replication, some of the phage genomes undergo homologous recombination with the cloned escape mutant DNA and generate phage that no longer contain the marker. Subsequent plating under restrictive conditions allows the growth of only recombinant phage. If those recombinants exhibit the escape phenotype, then the cloned DNA fragment must have contained escape mutations.