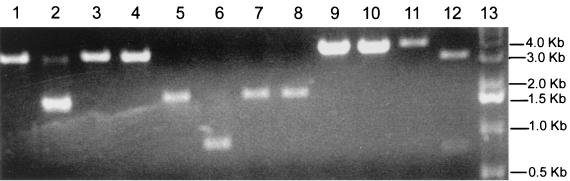
FIG. 7.
Restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of molecularly cloned virus. Cultures were infected with MHV-A59 or icMHV-A59#1, and intracellular RNA was isolated at 8 h p.i. With primer pairs and RT-PCR, cDNA amplicons were isolated that contained the various marker mutations that had been inserted into the component clones. The purified wild-type MHV-A59 and icMHV-A59#1 amplicons were restricted with Esp3I or RsrII and separated in 0.8% agarose gels. Lane 1, wild-type A59 amplicon from nucleotides 2020 to 5031, uncut; lane 2, wild-type A59 amplicon from nucleotides 2020 to 5031 digested with Esp3I; lane 3, icMHV-A59#1 amplicon from nucleotides 2020 to 5031, uncut; lane 4, icMHV-A59#1 amplicon from nucleotides 2020 to 5031, Esp3I digested; lane 5, wild-type A59 amplicon from nucleotides 16351 to 17875, uncut; lane 6, wild-type A59 amplicon from nucleotides 16351 to 17875 restricted with Esp3I; lane 7, icMHV-A59#1 amplicon from nucleotides 16351 to 17875, uncut; lane 8, icMHV-A59#1 amplicon from nucleotides 16351 to 17875 restricted with Esp3I; lane 9, wild-type A59 amplicon from nucleotides 22060 to 25416, uncut; lane 10, wild-type A59 amplicon from nucleotides 22060 to 25416 restricted with RsrII; lane 11, icMHV-A59#1 amplicon from nucleotides 22060 to 25416, uncut; lane 12, icMHV-A59#1 amplicon from nucleotides 22060 to 25416 restricted with RsrII; lane 13, 1-kb ladder.