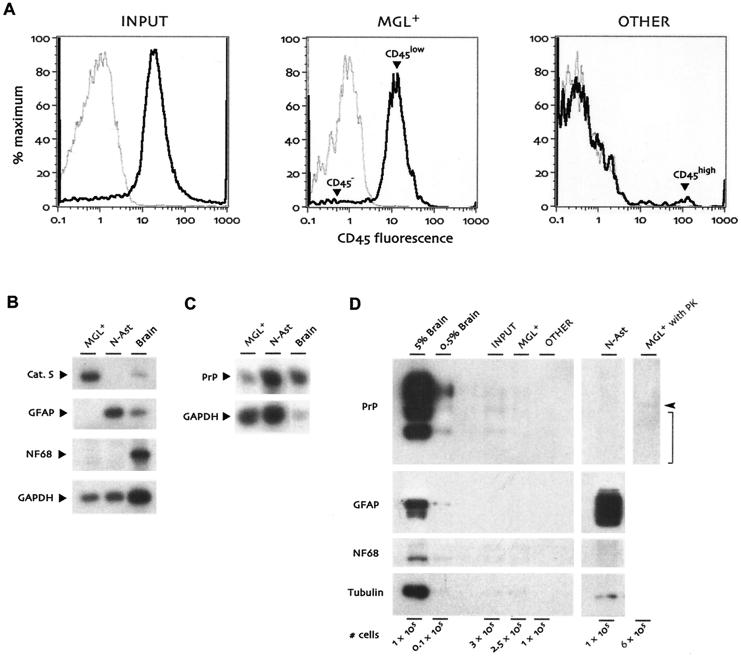
FIG. 1.
Characterization of cell populations isolated from end-stage CJD-infected mouse brains. (A) Flow cytometry histograms for CD45 (black lines) and an isotype control antibody (gray lines). Cells prior to CD11b magnetic column purification (Input, left panel) were already 80 to 85% CD45+. The positively selected MGL+ population (middle panel) was ∼95% CD45low microglia (arrowhead) after selection for CD11b+ cells, with very few CD45− nonleukocytic cells (arrowhead). The CD11b− flowthrough population (Other, right panel) was ∼90% CD45− with a few CD45high cells, probably lymphocytes from residual blood (arrowhead). CD11b− CD45high cells were not present in MGL+ and were not readily visible in the input population due to their very small numbers prior to column separation. (B) RT-PCR for microglial, astrocytic, and neuronal markers. RNAs from MGL+ cells, normal astrocyte cultures (N-Ast), and whole brain were analyzed in parallel for cathepsin S (Cat. S), GFAP, and neurofilament light chain (NF68). (C) PrP expression levels compared in microglia, astrocytes, and whole brain by semiquantitative RT-PCR. The amount of brain RNA in this assay was reduced so that all samples would be in the exponential phase of PrP amplification in parallel. (D) Analysis of cell populations on Western blots. The indicated number of cells from the Input, MGL+, and Other populations were compared with neonatal astrocytes as well as aliquots from 5% and 0.5% brain homogenates. Cell numbers shown for brain homogenates are based on an estimate of 109 cells per g of brain. Compared with brain, cells displayed little PrP or neurofilament light chain (NF68) expression, and GFAP could be seen only with extremely long film exposure, at least 50-fold reduced relative to that of starting whole brain. α-Tubulin was detected on the same blot for comparison between tubulin-rich neurons and microglial cells, which are relatively tubulin-poor. The final lane shows virtually undetectable levels of protease-resistant PrP (expected position indicated by bracket) in CJD-infected microglia that had been digested with proteinase K (PK). The arrowhead indicates the migration of proteinase K, which cross-reacts with the PrP antiserum.