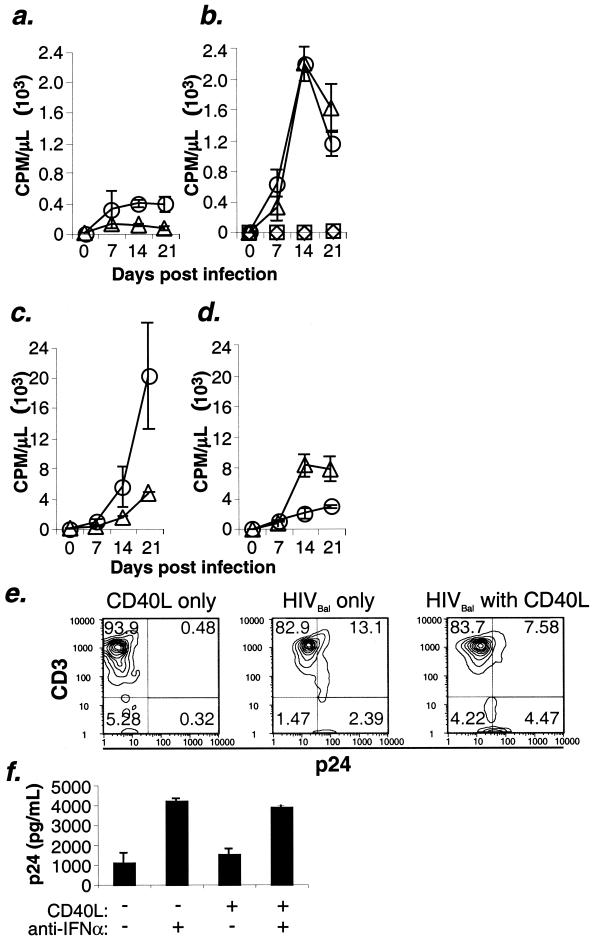
FIG. 6.
IPC transmit HIV to autologous CD4 T cells. (a) Following a 2-h exposure to either HIVLAI/IIIB (triangles) or HIVBaL (circles), 4 × 104 IPC were washed and then coincubated with 105 autologous CD4 T cells. Viral replication was assessed weekly for RT activity in triplicate cultures. (b) Infected IPC/T-cell cocultures were also incubated in the presence of CD40LT following exposure to HIV. CD4 T cells that were directly exposed to either HIVLAI/IIIB (squares) or HIVBaL (diamonds), washed, and cultured alone served as controls. Data shown correspond to those for cultures performed in parallel with experiments for Fig. 2 and are representative of three experiments. By comparison, MDC/CD4 T-cell cultures were assessed in parallel either without (c) or with (d) the addition of CD40LT. (e) IPC/T-cell cocultures incubated in the presence or absence of HIVBaL and/or CD40LT were assessed by flow cytometry for intracellular HIV p24 following 1 week of culture. (f) IPC/T-cell cocultures incubated in the presence or absence of neutralizing anti-IFN-α antibody were assessed for p24 production 1 week following exposure to HIVBaL.