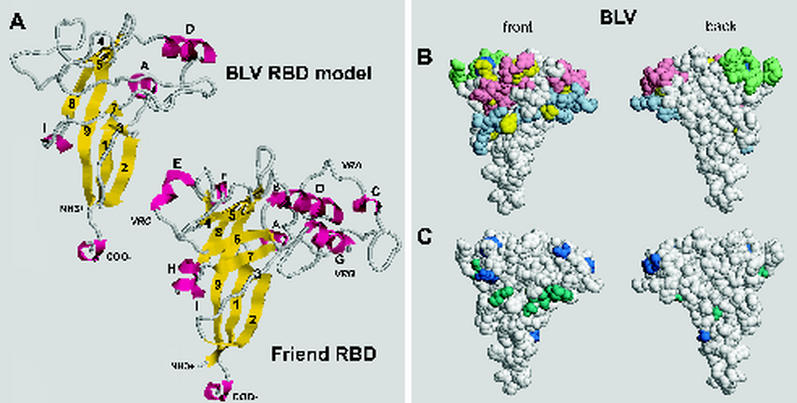
FIG. 7.
(A) Comparison of the proposed structure of the BLV RBD with a known structure (20) of the F-MuLV RBD monomer. Structures are depicted by using RasMol, version 2.7.1.1 (4, 57). Yellow, β strands; magenta, helices. Of the β strands predicted to be present in the BLV RBD, 1β, 2β, 4β, 8β, and 9β were modeled as such; 3β, 5β, and 7β were modeled as β-like structures, and 6β was not modeled. Of the predicted α helices, Aα, Dα, and Iα were modeled, whereas Eα and Gα were not. The BLV RBD has no helix analogous to Cα of F-MuLV. Coordinates for the BLV model and an annotated version of Fig. 7 are available from the corresponding author upon request. (B) Space-filling models of the BLV RBD illustrating the locations of the variant residues described in this paper (yellow) and the strain-specific Y108H of Bat2cl6 BLV (dark blue), as well as locations of peptides whose polyclonal antibodies neutralize infectivity or block fusion (10, 49). Pink, aa 72 to 81 and 111 to 125; light green, aa 97 to 106; light blue, aa 131 to 150. (C) Locations of strain-specific variant amino acids (A48T, A73P, K74R, S82F, Y108H, and R111H; dark blue) and amino acids varying in individual BLV isolates (S39F, S56F, S58A, D60N, Q95K, V140A, N141D, I144T, and H148Q; dark green) among complete BLV Env RBD sequences in the GenBank database. BLV Env sequences from K02120 (55) and M35242 (39) are the same as the those for the Bat2cl6 strain except for Y108. Accession numbers of BLV sequences encoding the depicted variants are K02251 (53); M35238, M35239, and M35240 (39); D00647 (13); S83530 (40); AF111171 (51); AF257515 (17); and AF067081.