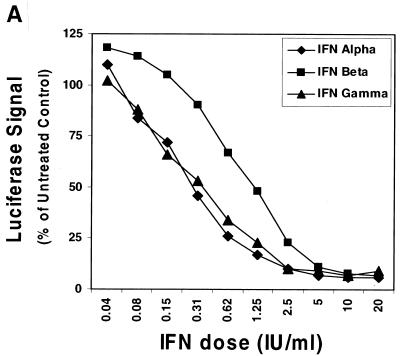
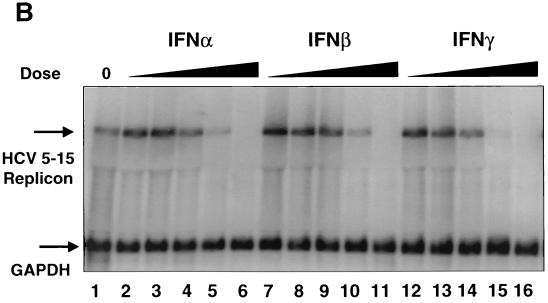
FIG. 1.
Inhibition of HCV RNA synthesis in the subgenomic replicon cells by IFN-α, -β, and -γ. (A) HCV replicon luciferase reporter cells (I389luc-ubi-neo/NS3-3′/5.1) were incubated in the presence of IFN-α, -β or -γ for 24 h and then assayed for luciferase activity. Luciferase signals were plotted as mean percentages of those for the untreated control cells and are representative of three independently derived experiments. (B) Northern blot analysis of HCV replicon RNA derived from I389neo/NS3-3′/wt replicon (16) cells treated with log increment doses of IFN-α (lanes 2 to 6) or IFN-γ (lanes 12 to 16) (0.01 to 100 IU/ml) or IFN-β (lanes 7 to 11) (0.003 to 33 IU/ml). A 32P-labeled, HCV-specific (NS5A-NS5B) probe was used to detect replicon RNA extracted from the replicon cells that had been treated with various doses of IFN for 72 h. Similarly, a probe specific for glyceraldehyde-3-phosphate dehydrogenase mRNA was used to monitor the level of this cellular RNA.