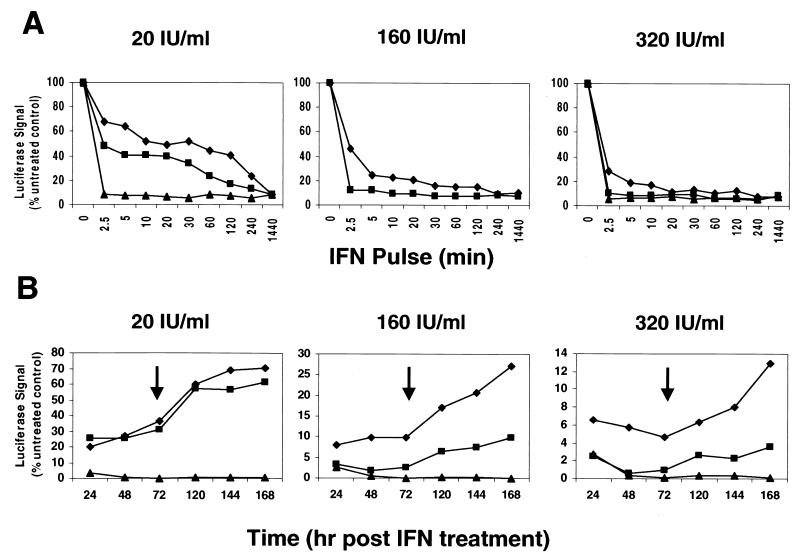
FIG. 2.
Differential response rates of HCV replicon reporter cells to IFN treatment and durability of IFN inhibitory effect. (A) HCV replicon reporter cells (I389luc-ubi-neo/NS3-3′/5.1) were treated with 20, 160, or 320 IU of IFN-α (diamonds) and IFN-β (squares)/ml or with 20 and 320 IU of IFNγ (triangles)/ml for various lengths of time (2.5 min to 24 h) and assayed for luciferase activity at the 24-h time point from the start of IFN treatment. Luciferase signals were plotted as mean percentages of the untreated control cells and are representative of three independently derived experiments. (B) Reporter cells were treated with IFN doses as described above for 4 h and then assayed for the luciferase signal 24, 48, or 72 h posttreatment. In addition, a parallel and equally treated cell culture was trypsinized at the 72-h mark (see arrow), diluted 1:4 into new microtiter plates, and subsequently assayed either 48, 72, or 96 h from this point (120, 144, and 168 total hours post-IFN treatment). Durability of the IFN HCV replication inhibitory effect was plotted over time as a percentage of the luciferase signal derived from mock-treated cells. Data represent means of triplicate values from a typical assay.