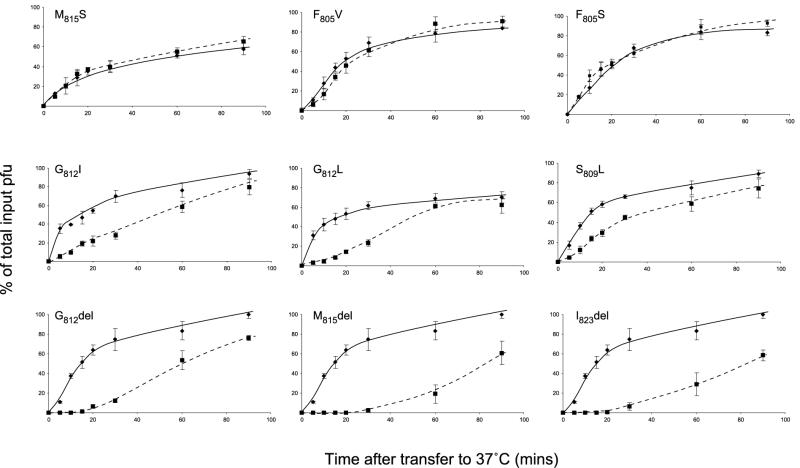
FIG. 4.
Entry rates of pseudotyped virions. Mutant or wild-type gH expression plasmids were transfected into cells which were then infected with a gH-negative mutant of HSV-1. The entry rate of pseudotyped infectious progeny was assessed by adsorbing approximately 300 PFU to monolayers of CR1 cells at 4°C, transferring cultures to 37°C, and inactivating residual inoculum by acid washing at various times after transfer. Plaques were then counted after incubation for a further 2 days. An estimate of the total available infectivity was obtained from cultures that received no acid treatment, and the number of plaques obtained following acid treatment at a particular time was recorded as a percentage of the total available. The entry rate of virions pseudotyped with mutant gH molecules  was compared in parallel cultures with the entry rate of virions pseudotyped with a wild-type gH molecule
was compared in parallel cultures with the entry rate of virions pseudotyped with a wild-type gH molecule  . The means and standard deviations of triplicate cultures are given. del, deleted.
. The means and standard deviations of triplicate cultures are given. del, deleted.