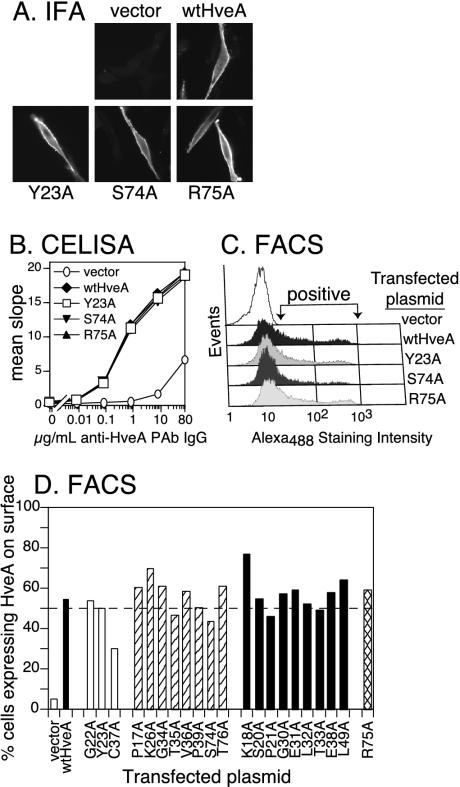
FIG. 3.
Expression of HveA mutant proteins on transfected cells. B78-H1 cells were transiently transfected with plasmids carrying each of the HveA mutants and evaluated for the expression of HveA after 48 h. (A) Cells were stained with fluorescently labeled anti-HveA PAb IgG and visualized by immunofluorescence microscopy to detect cell surface expression. Results for the transfection of wild-type HveA (wtHveA) and three representative HveA mutants are shown. (B) HveA expression was quantitated by CELISA. Cells were plated on 96-well plates and titrated with anti-HveA PAb IgG (R140) to estimate the level of cell surface expression. Sample data are shown for wild-type HveA and three representative HveA mutants. (C) Cells were stained with fluorescently labeled (Alexa Fluor 488) anti-HveA PAb IgG and analyzed by flow cytometry (FACS). Sample data for wild-type HveA and three representative HveA mutants show the level and range of positive staining. (D) Flow cytometry data for all of the HveA mutants are shown to indicate the percentage of cells staining positive for HveA. The dotted line represents 50% of the cells staining positive for HveA. Mutants were divided into four categories based on their ability to bind gD (see Fig. 4 and Table 1).