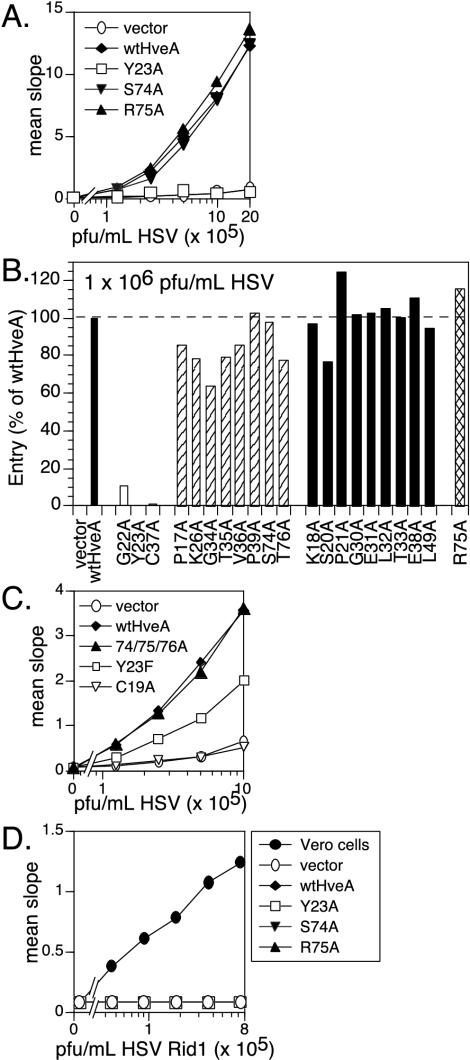
FIG. 5.
HveA mutant proteins mediating HSV entry into transfected cells. Transiently transfected B78-H1 cells expressing the HveA mutant proteins were seeded on 96-well plates, incubated with an HSV β-galactosidase reporter virus for 6 h, and assayed for β-galactosidase activity as a measure of virus entry. (A) Sample data show the ability of wild-type HveA (wtHveA) and three representative HveA mutants to mediate entry of increasing amounts of HSV. Assays detecting HveA expression and gDt binding were run in parallel (Fig. 3 and 4). (B) Data show the original panel of 21 HveA mutants mediating entry at one concentration of HSV. Mutants were divided into the categories based on gD binding phenotype (see Fig. 4 and Table 1). Data are expressed as a percentage of entry mediated by wild-type HveA. Results from one representative experiment are shown. (C) The ability of additional HveA mutants to mediate entry of increasing amounts of HSV is shown. (D) Sample data show the inability of wild-type HveA and three representative HveA mutants to mediate entry of increasing amounts of a mutant β-galactosidase reporter virus, HSV Rid1, after 6 h. Vero cells were included as a positive control for HSV Rid1 entry.