TABLE 1.
Structural and dynamical properties of cytochrome-c in two solvents
| Solvent: water | Solvent: glycerol/water (3:2 v/v) | |
|---|---|---|
| Protein* | ||
| (a) RMSD Cα/Å | 1.14 (0.23) | 0.87 (0.11) |
| (b) RMSD SC/Å | 1.89 (0.34) | 1.35 (0.18) |
| (c) SASphob/Å2 | 1581 (44) | 1486 (54) |
| (d) SASphil/Å2 | 4971 (136) | 4896 (97) |
| Solvent† | ||
| (e) nw | 4948 | 2030 |
| (f) ng | 721 | |
| (g) ρbulk/(g · cm−3) | 0.992 | 1.125 |
| Solvent shell‡ | ||
| (h) nSw | 673 (18) | 321 (8) |
| (i) nSg | 129 (5) | |
(j) 
|
6.1 (1.7)/— | 4.1 (1.5)/2.0 (1.4) |
(k) 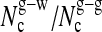
|
5.7 (1.9)/3.3 (1.3) | |
| Heme pocket§ | ||
| (l) nHp | 142 (4) | 140 (4) |
| (m) nHw | 15 (2) | 10 (2) |
(n) 
|
2.8 (0.6)/2.2 (0.6) | 1.9 (0.4)/0.8 (0.3) |
Values in parentheses are standard deviations.
Protein: (a) RMS deviations from the equilibrated structure and fluctuations of the Cα atoms; (b) RMS deviations from the equilibrated structure and fluctuations of the side-chain atoms; (c) solvent-accessible surface area (probe radius 1.6 Å) for hydrophobic residues; (d) solvent-accessible surface area (probe radius 1.6 Å) for hydrophilic residues.
Solvent: (e) number of water molecules; (f) number of glycerol molecules; and (g) bulk density.
Solvent shell: (h) average number of water molecules; (i) average number of glycerol molecules; (j) average coordination number of a water molecule to water (w-w) or glycerol (w-g) molecules; and (k) average coordination number of a glycerol molecule to water (g-w) or glycerol (g-g) molecules.
Heme pocket: (l) average number of nonhydrogen protein atoms; (m) average number of water molecules; and (n) average coordination number between a water molecule in the heme pocket to other water molecule in the heme pocket (Hw-Hw) and water molecules in the solvent shell (Hw-Sw).
