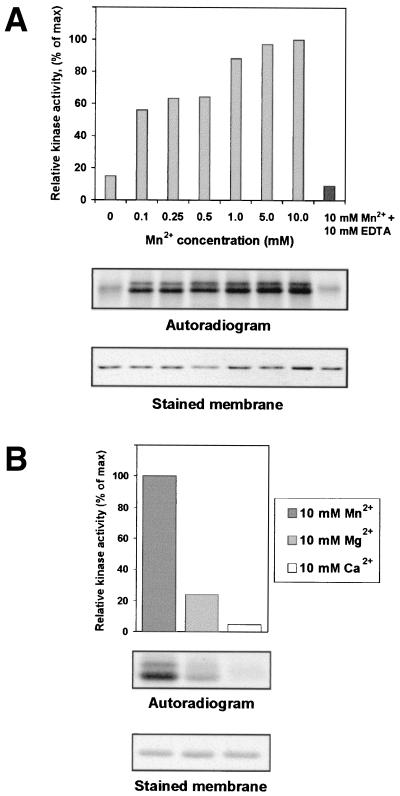
FIG. 1.
Phosphorylation of PVA VPg by plant protein kinase activity is stimulated by Mn2+. (A) Increasing concentrations of manganese were introduced into assays containing bacterially expressed PVA VPg, total protein kinase activity from leaves of N. tabacum, and [γ-33P]ATP. Phosphoproteins were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to membranes, and their positions were identified by staining with Ponceau S. Radioactivity associated with phosphoproteins was compared by PhosphorImager densitometry and plotted against Mn2+ concentration. In a control experiment, manganese was removed from phosphorylation reaction in a 1:1 molar complex with EDTA. (B) Effect of Mn2+, Mg2+, or Ca2+ on phosphorylation of PVA VPg. Proteins were assayed for phosphorylation in a reconstituted system containing plant enzymes, [γ-33P]ATP, and 10 mM Mn2+, Mg2+, or Ca2+. Proteins were subjected to SDS-PAGE and transferred to membranes. Autoradiograms of phosphorylated proteins are shown together with stained membranes.