FIGURE 1.
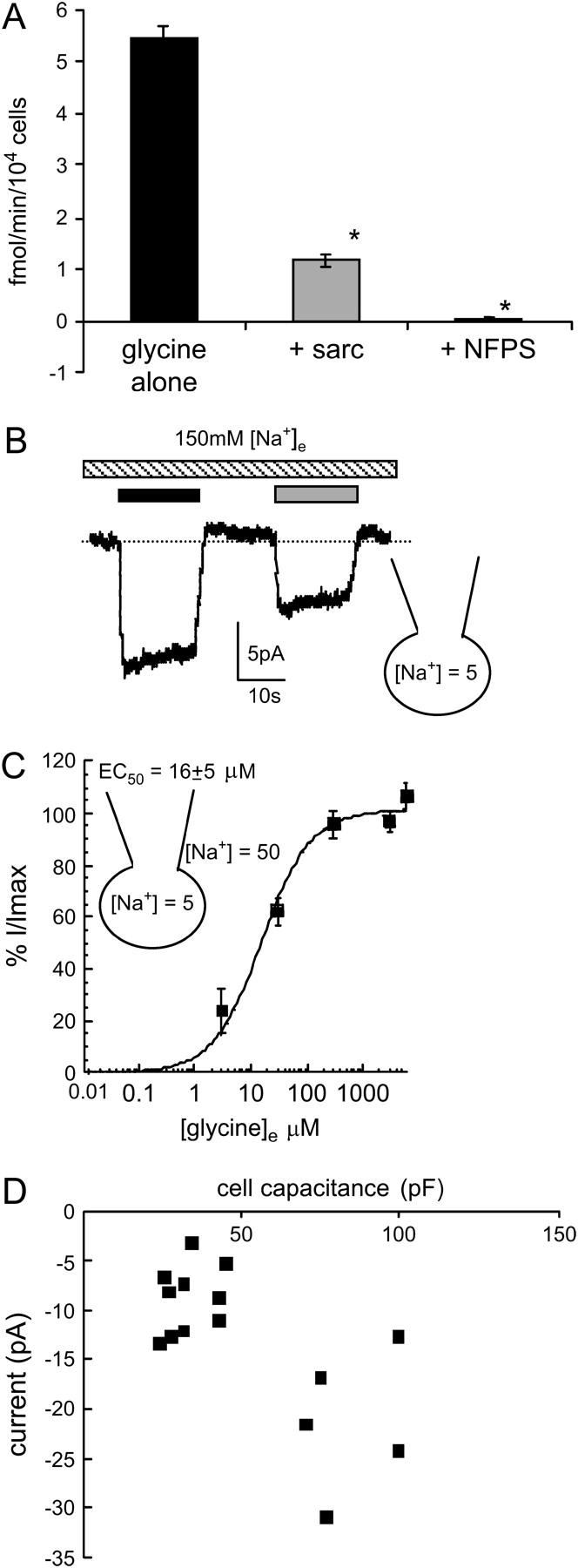
Glycine transport currents in CHO cells transfected with GLYT1b. (A) 3H-glycine uptake by CHO-GLYT1b cells (black bar); in the presence of the competitive GLYT1 substrate sarcosine (300 μM, shaded bar); and the GLYT1 specific inhibitor NFPS (1 μM, open bar) (n = 6, ANOVA). (B) A whole-cell patch-clamp recording at 0 mV of GLYT1b mediated currents. Sarcosine (300 μM, shaded bar) elicits a current that is smaller in amplitude than the current induced by glycine (300 μM, black bar). (C) Glycine concentration-response curve for transport currents mediated by CHO-GLYT1b cells voltage clamped at 0 mV. Glycine transport currents were normalized to the maximal current of each cell and fitted to the Michaelis-Menten equation (n = 10). (D) Correlation between cell capacitance and peak current amplitude (n = 15).
