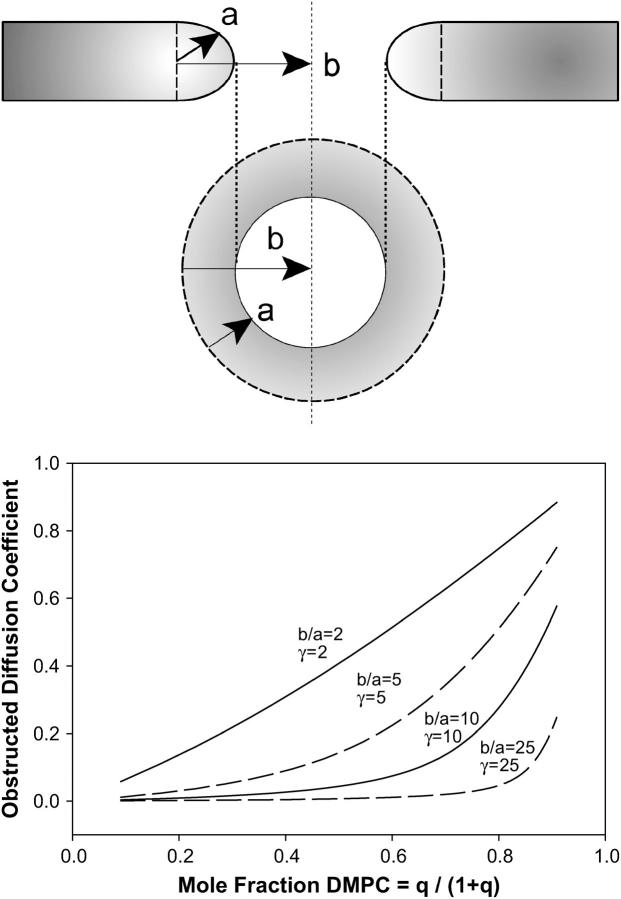
FIGURE 7.
Obstruction effects for the perforated lamellae model of bicelle morphology and the predicted effects on PEG-lipid lateral diffusion. The perforated lamellae model posits the presence of DHPC-rich toroidal holes perforating the DMPC-rich bilayer lamella. In the schematic at the top, the toroidal holes are modeled in terms of an annulus of DHPC with radial dimension a and overall radius b, thereby permitting an evaluation of their fractional surface coverage as described in the text, in turn permitting an estimate of obstruction effects on lateral diffusion for a given mole fraction of DMPC and a particular mobility γ of the PEG-lipid relative to the toroidal hole. The graph shows the predicted apparent decrease in PEG-lipid lateral diffusion from such an obstruction model for various dimensions and mobilities of the toroidal holes as a function of the mole fraction of DMPC. Note that only relatively small, mobile holes yield lateral diffusion coefficients near those observed experimentally.