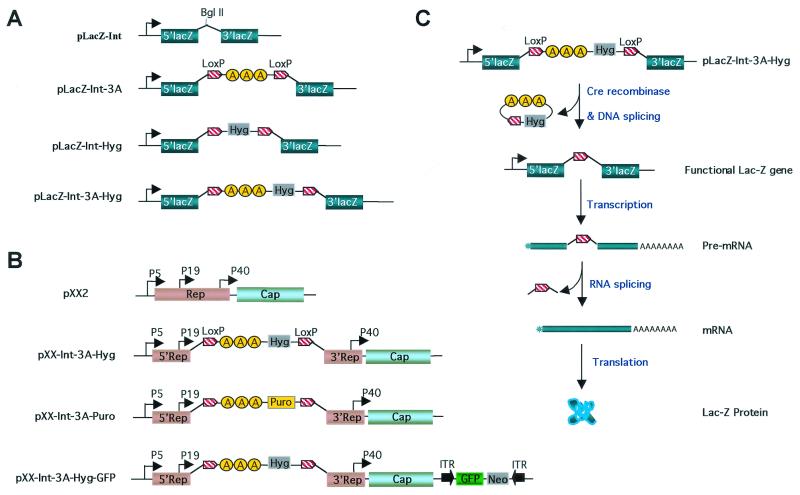
FIG. 1.
Construction of dual-spicing switch plasmids for gene expression control of lacZ and AAV rep genes. (A) Construction of dual-spicing lacZ plasmids. For pLacZ-Int, the lacZ gene contains an hCG intron insertion in the coding sequence (31). The BglII site is for cloning purpose. For pLacZ-Int-3A, a triple SV40 poly(A) cassette (3A) flanked by two loxP sequences was inserted into the BglII site in the hCG intron of pLacZ-Int to block lacZ gene transcription. For pLacZ-Int-Hyg, the Hygr gene flanked by two loxP sequences was inserted into the BglII site of pLacZ-Int. For pLacZ-Int-3A-Hyg, the triple SV40 poly(A), together with the Hygr gene flanked by two loxP sequences, was inserted into the BglII site of the pLacZ-Int. (B) Construction of dual-splicing switch AAV packaging plasmids. pXX2 is an AAV type 2 packaging plasmid (38). For pXX2-Int-3A-Hyg, the 3.2-kb termination cassette (Int-3A-Hyg) from plasmid pLacZ-Int-3A-Hyg was inserted into the shared Rep coding sequence downstream of promoter p19 to block rep gene transcriptions. For pXX2-Int-3A-Puro, the Hygr gene was replaced by Puror gene for additional selection. For pXX2-Int-3A-Hyg-GFP, an AAV GFP vector which contains a CMV promoter-driven EGFP gene and a neomycin-resistant gene was inserted into the SseI site of pXX2-Int-3A-Hyg plasmid. (C) Activation of lacZ gene controlled by the dual-splicing switch. A Cre recombinase is provided in trans by an adenovirus infection. The enzyme recognizes the two loxP sites and splices out the inserted DNA fragment that contains the poly(A) sequences between the loxP sites. The removal of poly(A) sequences then allows transcription to proceed and full-length mRNA is generated. After RNA splicing, the inserted intron is precisely removed from the full-length mRNA, and the coding sequence is restored.