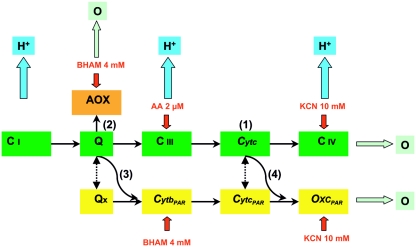
FIG. 1.
Simplified figure (adapted from the work of Milani et al. [7]) of the respiratory network in C. parapsilosis mitochondria, which includes three terminal oxidases and four electron transport pathways. The CRC consists of Q, complex I (C i), complex III (C iii), and complex IV (C iv; cytochrome c [Cytc] oxidase), as shown in the green boxes. A secondary PAR comprises alternative ubiquinone (Qx), cytochrome b (CytbPAR), cytochrome c (CytcPAR), and secondary terminal oxidase (OxcPAR) insensitive to AA but inhibited by BHAM and cyanide, as shown in the yellow boxes. A cyanide-resistant AOX branches at the Q level, as shown in the orange box. The numbers in parentheses show the four electron transport pathways, the blue arrows indicate sites of H+ pumping, the red arrows indicate targets of the inhibitors (AA, BHAM, and cyanide), and the dotted lines depict putative interactions.