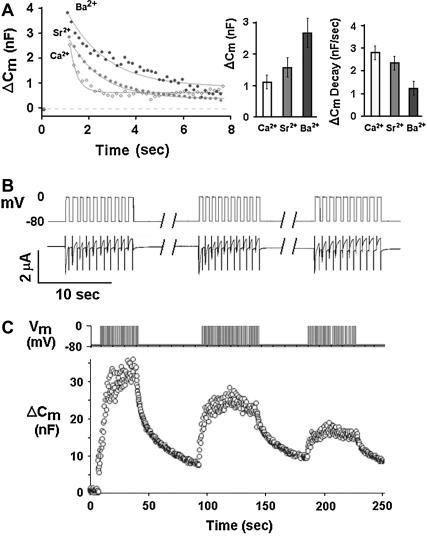
FIGURE 5.
Differential effects of Ca2+, Sr2+, or Ba2+ on depolarization-induced Cm changes, and vesicle depletion by repetitive stimulation (A) Differential effects of Ca2+, Sr2+, or Ba2+ on depolarization-induced exocytosis. Oocytes expressing Cav1.2, syntaxin 1A, syt-1, and SNAP-25 (excitosome). (Left panel) Original traces showing time course of Cm upon depolarization, fitted by simple exponentials; (middle panel) instantaneous depolarization-induced Cm increase in Ca2+, Sr2+, and Ba2+ (mean ± SE, n = 10, each); and (right panel) rate of compensatory Cm decrease (mean ± SE, n = 10, each). As compared to Ca2+, the instantaneous Cm increase was greater in Ba2+ (middle panel), and the compensatory Cm decrease was slower (right panel). In Sr2+, the respective values were between those of Ca2+ and Ba2+. (B) Current amplitude during repeated trains of membrane depolarization. Oocytes were depolarized by three trains composed of 10 depolarizations from −80 to 0 mV 1 s each (upper panel). Depolarization-induced inward current inactivated during trains whereas no run-down of current amplitude was observed from one train to the other (lower panel). (C) Exhaustibility of depolarization-induced capacitance changes. Repeated depolarization pulses from −80 mV to 0 mV for 1 s each (upper trace) and the associated Cm changes (lower trace). Data are consistent with depletion and only partial replenishing of a pool of releasable vesicles.