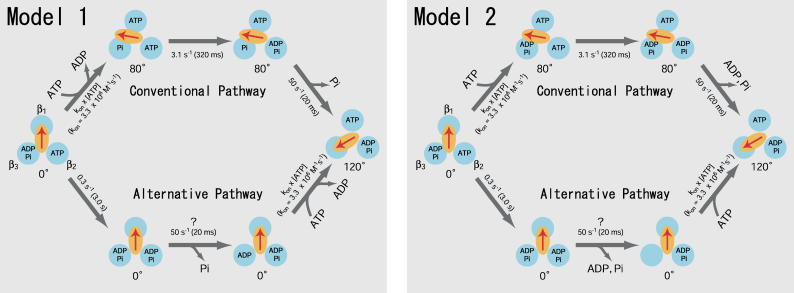
FIGURE 3.
Two models of the reaction pathways of the ATP-hydrolysis reaction in F1(β-E190D). F1(β-E190D) are represented as three β-subunits (blue) and a γ-subunit (orange oval with an arrow). The rate constants obtained from this work and the previous works (11) are shown. The rate constant 50 s−1 is assumed to be unchanged between the conventional and alternative pathway. The models represent the pathways of F1(β-E190D) but the wild-type F1 probably has similar alternative pathways as well (see the text). (Model 1) ADP is released during the rotary motion upon ATP-binding. (Upper path) The conventional pathway. (Lower path) The alternative pathway. (Model 2) ADP release and ATP binding occur at a different stage in the reaction pathway. (Upper path) The conventional pathway. The 40° substep rotation is coupled with release of the products. (Lower path) The alternative pathway. The products are released without accompanying rotation. Note that occupancy of the catalytic sites by ATP (or ADP) during catalysis in this alternative pathway is one or two (bisite catalysis).