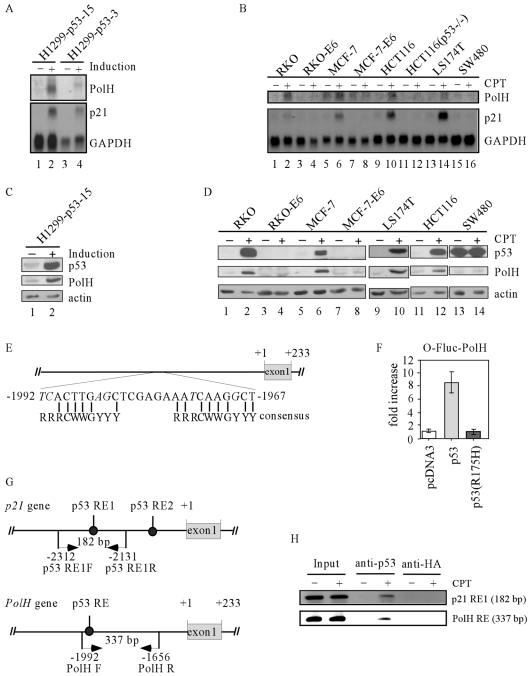
FIG. 1.
PolH is a p53 target gene. (A) PolH is induced by p53. Northern blots were prepared using total RNA isolated from H1299 cells that were uninduced and induced to express p53 for 24 h. The blots were probed with cDNAs derived from the PolH, p21, and GAPDH genes, respectively. (B) PolH is induced in cells by CPT in a p53-dependent manner. The experiment was performed as in panel A. (C) PolH expression is up-regulated by p53. Western blots were prepared using cell extracts purified from H1299 cells that were uninduced and induced to express p53. The HA-tagged p53 was detected with anti-HA. PolH was detected with anti-PolH polyclonal antibody. Actin was determined as loading controls. (D) PolH expression is up-regulated in cells by CPT in a p53-dependent manner. (E) Schematic presentation of the PolH genomic structure. A potential p53-responsive element is located 1,965 nucleotides upstream of the PolH transcription starting site. The consensus p53-responsive element is shown for comparison. Mismatched nucleotides are indicated in italics. (F) The potential p53-binding site is responsive to p53 but not to p53(R175H). A DNA fragment containing the potential p53-binding site was cloned into the luciferase reporter O-Fluc. The resulting construct was designated O-Fluc-PolH. O-Fluc-PolH was cotransfected into H1299 cells with a pcDNA3 control vector or a vector that expresses p53 or p53(R175H). (G) Schematic presentation of the PolH and p21 promoters with the location of the transcriptional start site, p53-responsive elements, and primers used for ChIP assays. (H) p53 directly binds to the potential p53 response element within the PolH promoter. The ChIP assay was performed as described in Materials and Methods. p53-DNA complexes were captured with anti-p53. Anti-HA antibody was used as a control. The fragment containing the p53 response element in PolH was amplified by PCR with primers PolH-F and PolH-R. The fragment containing the p53 response element 1 in p21 was amplified by PCR as a control.