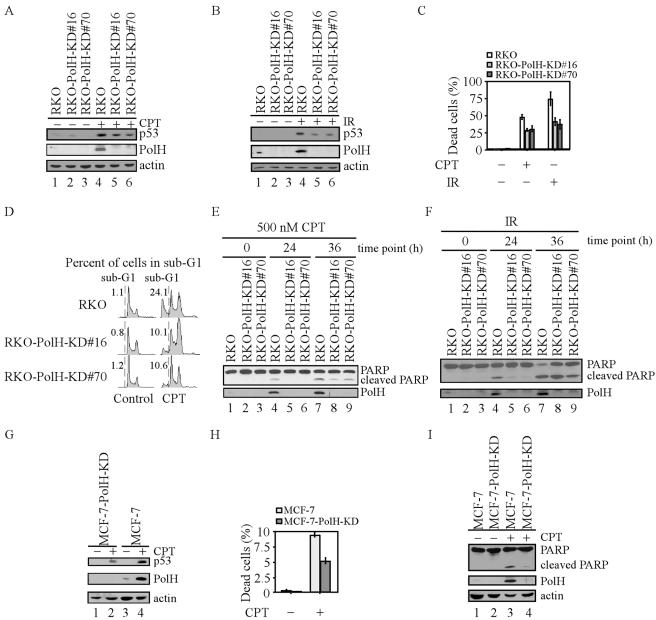
FIG. 2.
Knockdown of PolH gives cells resistance to CPT- and IR-induced apoptosis. (A and B) PolH is knocked down in RKO-PolH-KD cells. RKO or RKO-PolH-KD cells were untreated or treated with 300 nM CPT for 6 h (A) or with 10 Gy of IR (B). p53 was detected with anti-p53 polyclonal antibody. Actin was also examined as a loading control. (C) RKO-PolH-KD cells are less sensitive than RKO to cell death induced by various DNA damage agents. RKO and RKO-PolH-KD were treated with 500 nM CPT for 12 h or 20 Gy of IR. Three days following treatment, both floating cells in the medium and attached cells on the plates were collected. Cells were stained with trypan blue dye for 15 min. Unstained cells (live cells) and stained cells (dead cells) were counted separately. (D) RKO-PolH-KD cells are more resistant than the parental RKO cells to CPT-induced apoptosis. Cells were treated as in panel C and then collected and stained with propidium iodide for DNA histogram analysis. (E and F) PARP cleavage is decreased in RKO-PolH-KD cells after treatment with various DNA damage agents. Both RKO and RKO-PolH-KD cells were treated with 500 nM CPT (E) or 20 Gy of IR (F). At indicated times after treatment, cells were collected and intact PARP, cleaved PARP, and PolH were detected by Western blot analysis. (G) PolH is knocked down in MCF-7-PolH-KD cells. MCF-7 and MCF-7-PolH-KD cells were treated with 300 nM CPT for 6 h. p53, PolH, and actin were detected by Western blot analysis. (H) MCF-7-PolH-KD cells are less sensitive than the parental MCF-7 cells to CPT-induced cell death. Cells were treated and the trypan blue dye exclusion assay was performed as in panel C. (I) PARP cleavage is decreased in MCF-7-PolH-KD cells after DNA damage. Cells were treated and Western blot analysis was performed as in panel E.