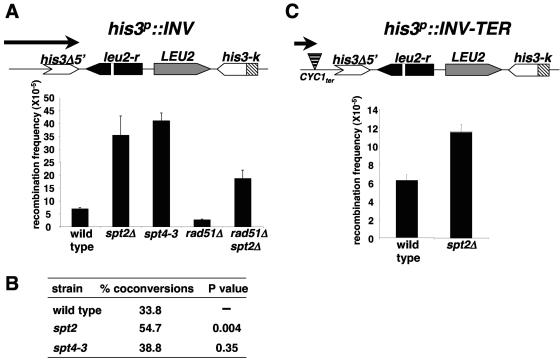
FIG. 8.
An spt2Δ mutation increases recombination between inverted repeats. (A) Measurement of recombination using the hi3p::INV inverted repeat system (1). The structure of the inverted repeats is diagrammed at the top. In each experiment, six separate colonies from wild-type (M137-11B), spt2Δ (L1096), spt4-3 (M236-12D), rad51Δ (L1099), and rad51Δ spt2Δ (L1100) strains were independently grown to saturation in YPD and plated on either synthetic complete medium or medium lacking histidine. The frequency of recombination for each independent culture is equal to the frequency of His+ colonies. The recombination frequencies shown are the averages and standard errors from three experiments. (B) spt2Δ increases coconversion events. The percentage of coconversion was determined by calculating the ratio of His+ Leu− colonies to His+ Leu+ colonies. In each experiment, six separate colonies were tested, and the values shown are the averages and standard errors from three experiments. (C) Reducing transcription through the his3p::INV inverted repeats decreases spt2Δ hyperrecombination. The recombination frequency was calculated for wild-type (ITE-1C) or spt2Δ (L1101) strains containing the his3p::INV TER (diagrammed at the top). This construct has a CYC1 terminator inserted before the his3-5′Δ sequence, reducing transcription through the inverted repeat cassette (30). The recombination frequencies were calculated as described for panel A.