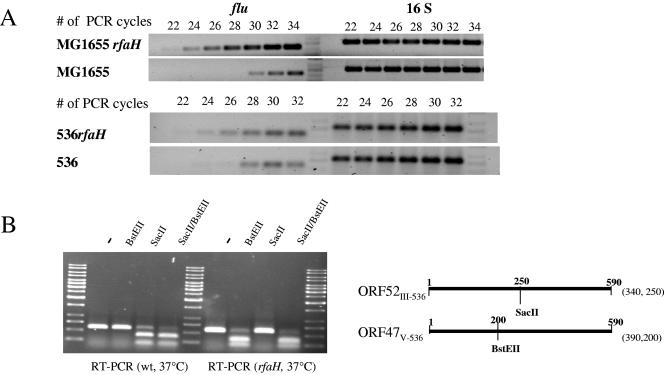
FIG. 4.
Comparison of flu transcript levels of E. coli wild-type strains and their rfaH derivatives. (A) Comparison of flu transcript levels of uropathogenic E. coli strain 536 and K-12 strain MG1655. The uropathogenic and K-12 wild-type strains, as well as their rfaH mutants, were cultivated at 37°C. The flu transcript levels of exponentially growing, planktonic cells were compared by RT-PCR. 16S RNA levels were used as internal controls of the quantity of RNA used for RT-PCR. (B) Comparison of the flu ortholog transcript levels of uropathogenic E. coli strain 536 and its rfaH mutant. The strains were cultivated at 37°C. The ORF52III-536 and ORF47V-536 transcripts of exponentially growing, planktonic cells were reverse transcribed and amplified by RT-PCR. The cDNA was consecutively digested with SacII and BstEII in order to distinguish between the ORF52III-536- and ORF47V-536-specific cDNA fractions. The resulting restriction fragments were separated on an agarose gel. The localization of the SacII and BstEII restriction sites and the sizes of the resulting cDNA fragments are indicated. wt, wild type.