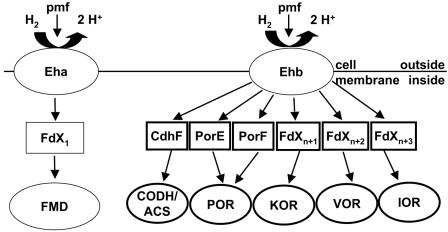
FIG. 3.
Working model for the role of Ehb in generation of low-potential electron donors in M. maripaludis. The cellular membrane contains two energy-conserving [NiFe] hydrogenases, Eha and Ehb. Eha is proposed to be coupled to FMD, a key enzyme in methanogenesis from CO2, via an unidentified ferredoxin, FdX1. Ehb is proposed to be coupled to CODH-ACS, a key enzyme in autotrophic CO2 fixation, and a number of ferredoxin-dependent oxidoreductases that catalyze important anabolic reactions, including POR, 2-ketoglutarate oxidoreductase (KOR), branched-chain VOR, and indole-pyruvate oxidoreductase (IOR). Ferredoxins that may be involved in coupling these enzymes to Ehb include CdhF, PorE, and PorF. FdX2, FdX3, and FdX4 are unidentified ferredoxins.