TABLE 2.
Number of protons linked to the binding of paromomycin to the E. coli 16 S rRNA A-site model oligonucleotide at pH 6.8
| Buffer (10 mM) | ΔHion* (kcal/mol) | ΔHobs† (kcal/mol) | ΔHint‡ (kcal/mol) | Δndrug‡ | fdrug§ (Sulfate salt) | fdrug§ (Free base) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cacodylate | −0.47 | −12.5 ± 0.1 | −12.1 ± 0.1 | 0.88 ± 0.03 | 0.43 ± 0.01 | 0.83 ± 0.03 |
| TES | +7.83 | −5.2 ± 0.1 |
Ionization heats (ΔHion) at 25°C for the indicated buffers were taken from Fukada and Takahashi (52).
ΔHobs values were derived from fits of the ITC profiles shown in Fig. 6 C, with the indicated uncertainties reflecting the standard deviations of the experimental data from the fitted curves.
Values of ΔHint and Δndrug were determined using Eqs. 6a and 6b, with the indicated uncertainties reflecting the maximum errors in ΔHobs as propagated through these equations.
Values of fdrug were calculated from the 15N NMR-derived pKa values for the sulfate salt and free base forms of paromomycin using the Henderson-Hasselbalch relationship: 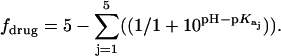 In this relationship,
In this relationship, 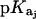 is the pKa value for the jth amino group. The indicated uncertainties in fdrug reflect the maximum errors in the NMR-derived pKa values as propagated through the above relationship.
is the pKa value for the jth amino group. The indicated uncertainties in fdrug reflect the maximum errors in the NMR-derived pKa values as propagated through the above relationship.
