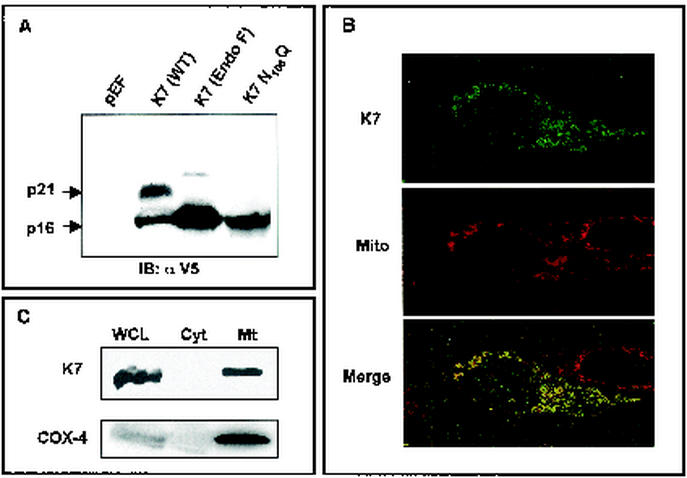
FIG. 1.
Identification of K7 and its localization. (A) Identification and glycosylation of K7. At 48 h after transfection with pEF or pEF-K7, 293T cells were lysed by lysis buffer. Whole-cell lysates (WCL) were used for the immunoblot (IB) assay with anti-V5 antibody. Lanes (from left to right): WCL of 293T cells transfected with pEF; WCL of 293T cells transfected with pEF-K7-V5; WCL of 293T cells transfected with pEF-K7-V5 with N-glycosidase F treatment for 12 h; WCL of 293T cells transfected with pEF-K7 N108Q. Arrows indicate the 16- and 21-kDa K7 proteins. (B) Mitochondrial localization of K7 protein. After staining with Mitotracker (red), 293T cells expressing K7 protein were fixed, permeabilized, and reacted with anti-V5 antibody and Alexa 488-conjugated anti-mouse secondary antibody (green). Immunofluorescence was examined using a Leica confocal immunofluorescence microscope, and a single representative optical section is presented. The yellow areas in the merged panel indicate colocalization of the red and green labels. (C) Subcellular fractionation of K7. 293T cells expressing K7 were used for subcellular fractionation as described in Materials and Methods. Whole-cell lysates (WCL), cytosolic fraction (Cyt), and mitochondrial fraction (Mt) were used for an immunoblot assay with anti-V5 and anti-COX-4 antibodies.