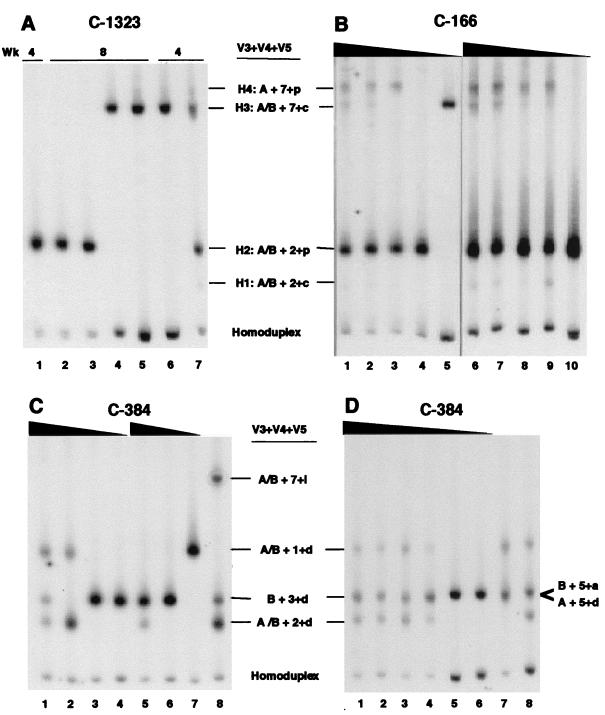
FIG. 3.
Virus populations identified by QHDA in chimpanzees inoculated with HIV-1/JC499 by different routes. The JC6 probe was mixed separately with bulk PCR products amplified from proviral DNA in chimpanzee cells. (A) PBMC (lanes 1, 2, 6, and 7) and lymph node (lanes 3, 4, and 5) samples obtained from C-1323 at 4 and 8 weeks after penile inoculation. (B) PBMC obtained from C-166 at 6 weeks after cervicovaginal inoculation. Two independent limiting dilutions are shown (lanes 1 to 5 and 6 to 10). (C and D) PBMC obtained from C-384 at 1 (C) and 2 (D) weeks after intravenous infection. Samples in lanes below solid triangles are PCR products from independent limiting dilution series of genomic DNA instead of independent PCRs. The heteroduplex populations detected in panel C, lane 8, were products from a PCR in which 2 μg of DNA was used as template. In panel D, lanes 7 and 8, heteroduplexes from products of two independent PCRs, using 0.85 μg of DNA in each, are shown. The amount of DNA used for the five independent limiting dilution series shown in panels B, C, and D ranged from 1 μg (maximum) to 0.0016 μg (at the highest dilution). The specific V3, V4, and V5 region combinations (see Table 2) represented by the various heteroduplexes were determined by sequence analysis and are indicated. In panel D, in the heteroduplexes identified as B + 3+d, two additional populations (B + 5+a and A + 5+d) were identified after sequencing.