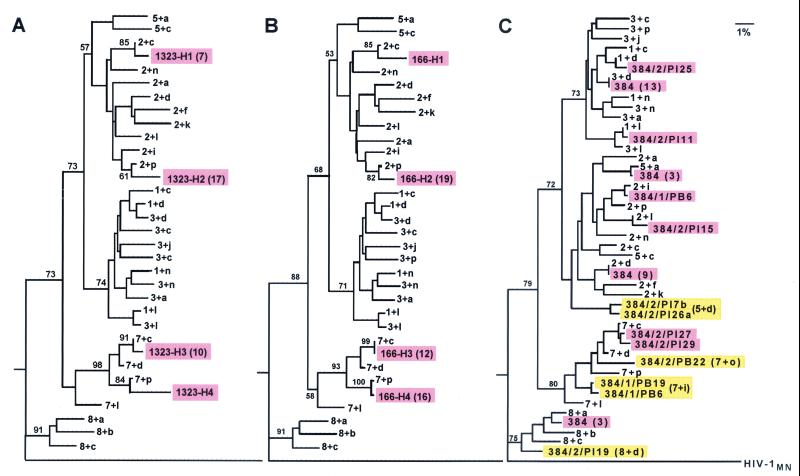
FIG. 4.
Phylogenetic trees of V4-plus-V5 populations in the HIV-1/JC499 inoculum and transmitted by the penile (A), cervical (B), and intravenous (C) routes to chimpanzees C-1323, C-166, and C-384, respectively. Transmitted populations are identified by shaded boxes. Numbers in parentheses indicate the number of individual sequences within one population for which a consensus sequence was used to generate the trees; otherwise, individual sequences were used. In panel C, the first numbers shown after “384/” indicate the week after inoculation when the sample was obtained, the tissue (Pl, plasma; PB, PBMC) of origin, and the individual clone number. The clones identified by pink boxes were those in the inoculum, whereas the yellow boxes identify clones with V4-plus-V5 populations (in parentheses) not found in the inoculum.